The clinical implication of psychiatric illnesses in patients with alcoholic liver disease: an analysis of US hospitals
- PMID: 35708303
- PMCID: PMC9344485
- DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2022.2090337
The clinical implication of psychiatric illnesses in patients with alcoholic liver disease: an analysis of US hospitals
Abstract
Background: In this study, we evaluate the clinical impact of psychiatric illnesses (PI) on the hospital outcomes of patients admitted with alcoholic liver disease (ALD).
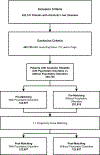
Methods: From the National Inpatient Sample from 2012-2017, patients with alcoholic cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis were selected and stratified using the presence/absence of PI (which was a composite of psychiatric conditions). The cases were propensity score-matched to PI-absent controls and were compared to the following endpoints: mortality, death due to suicide, length of stay (LOS), hospitalization charges, and hepatic complications.
Results: After matching, there were 122,907 PI with and 122,907 without PI. Those with PI were younger (51.8 vs. 51.9 years p = 0.02) and more likely to be female (39.2 vs. 38.7% p = 0.01); however, there was no difference in race. Patients with PI had lower rates of alcoholic cirrhosis but higher rates of alcoholic hepatitis/alcoholic hepatic steatosis. In multivariate, patients with PI had lower rates of all-cause mortality (aOR 0.51 95%CI 0.49-0.54); however, they experienced higher rates of deaths due to suicide (aOR 3.00 95%CI 1.56-5.78) and had longer LOS (aOR 1.02 95%CI 1.01-1.02).
Conclusion: Presence of PI in ALD patients is associated with prolonged hospital stay and higher rates deaths due to suicide.
Keywords: Alcoholic hepatitis; PI; anxiety; bipolar disorder; depression; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest Statement:
DU Lee was funded by NIH NIDDK T32 DK067872–17. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Alcoholic liver diseases].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2005 Dec 16;130 Suppl 5:S223-5. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2005. PMID: 16435717 German. No abstract available.
-
Incidence, survival and cause-specific mortality in alcoholic liver disease: a population-based cohort study.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug;51(8):961-6. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2016.1157889. Epub 2016 May 16. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27181618
-
The Impact of Malnutrition on the Hospital and Infectious Outcomes of Patients Admitted With Alcoholic Hepatitis: 2011 to 2017 Analysis of US Hospitals.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr 1;56(4):349-359. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001528. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 33769393
-
Prevalence and natural history of alcoholic liver disease.Clin Liver Dis. 2012 Nov;16(4):659-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2012.08.001. Clin Liver Dis. 2012. PMID: 23101975 Review.
-
Characteristic features of alcoholic liver disease in Japan: a review.Gastroenterol Jpn. 1993 Feb;28(1):137-48. doi: 10.1007/BF02775019. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1993. PMID: 8440419 Review.
Cited by
-
The prognostic impact of psychiatric intervention on alcohol-associated liver disease: The UK Biobank cohort study.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):929-942. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0278. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39188230 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants in People With Chronic Liver Disease and Depression: When Are They Warranted and How to Choose the Suitable One?J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024 Jul-Aug;14(4):101390. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2024.101390. Epub 2024 Feb 27. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38515504 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Callahan EJ, Jaén CR, Crabtree BF, Zyzanski SJ, Goodwin MA, Stange KC. The impact of recent emotional distress and diagnosis of depression or anxiety on the physician-patient encounter in family practice. J Fam Pract. 1998;46(5):410–418. - PubMed
-
- Hahn SR. Physical symptoms and physician-experienced difficulty in the physician-patient relationship. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134(9 Pt 2):897–904. - PubMed
-
- el-Serag HB, Kunik M, Richardson P, Rabeneck L. Psychiatric disorders among veterans with hepatitis C infection. Gastroenterology. 2002;123(2):476–482. - PubMed
-
- Blader JC. Acute inpatient care for psychiatric disorders in the United States, 1996 through 2007. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68(12):1276–1283. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
