Synthetic Heparan Sulfate Hydrogels Regulate Neurotrophic Factor Signaling and Neuronal Network Activity
- PMID: 35708492
- PMCID: PMC10108098
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c01575
Synthetic Heparan Sulfate Hydrogels Regulate Neurotrophic Factor Signaling and Neuronal Network Activity
Abstract
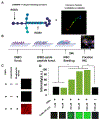
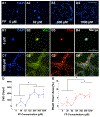
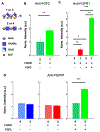
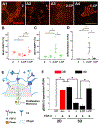
Three-dimensional (3D) synthetic heparan sulfate (HS) constructs possess promising attributes for neural tissue engineering applications. However, their sulfation-dependent ability to facilitate molecular recognition and cell signaling has not yet been investigated. We hypothesized that fully sulfated synthetic HS constructs (bearing compound 1) that are functionalized with neural adhesion peptides will enhance fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2) binding and complexation with FGF receptor-1 (FGFR1) to promote the proliferation and neuronal differentiation of human neural stem cells (hNSCs) when compared to constructs with unsulfated controls (bearing compound 2). We tested this hypothesis in vitro using 2D and 3D substrates consisting of different combinations of HS tetrasaccharides (compounds 3 and 4) and an engineered integrin-binding chimeric peptide (CP), which were assembled using strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloaddition (SPAAC) chemistry. Results indicated that the adhesion of hNSCs increased significantly when cultured on 2D glass substrates functionalized with chimeric peptide. hNSCs encapsulated in 1-CP hydrogels and cultured in media containing the mitogen FGF2 exhibited significantly higher neuronal differentiation when compared to hNSCs in 2-CP hydrogels. These observations were corroborated by Western blot analysis, which indicated the enhanced binding and retention of both FGF2 and FGFR1 by 1 as well as downstream phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) and enhanced proliferation of hNSCs. Lastly, calcium activity imaging revealed that both 1 and 2 hydrogels supported the neuronal growth and activity of pre-differentiated human prefrontal cortex neurons. Collectively, these results demonstrate that synthetic HS hydrogels can be tailored to regulate growth factor signaling and neuronal fate and activity.
Keywords: ERK; FGF2; click chemistry; neural stem cells; synthetic heparan sulfate hydrogel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuritogenic glycosaminoglycan hydrogels promote functional recovery after severe traumatic brain injury.J Neural Eng. 2024 Jun 27;21(3):036058. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad5108. J Neural Eng. 2024. PMID: 38806019 Free PMC article.
-
2-O Heparan Sulfate Sulfation by Hs2st Is Required for Erk/Mapk Signalling Activation at the Mid-Gestational Mouse Telencephalic Midline.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 15;10(6):e0130147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130147. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26075383 Free PMC article.
-
Heparan sulfate alterations in extracellular matrix structures and fibroblast growth factor-2 signaling impairment in the aged neurogenic niche.J Neurochem. 2017 Aug;142(4):534-544. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14081. Epub 2017 Jun 20. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 28547849
-
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans function as receptors for fibroblast growth factor-2 activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2.Circ Res. 2004 Feb 20;94(3):316-23. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000112965.70691.AC. Epub 2003 Dec 18. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 14684627
-
Heparan sulfate regulates the anabolic activity of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast cells by induction of Runx2.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Jan;210(1):38-50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20813. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17051597
Cited by
-
Neuritogenic glycosaminoglycan hydrogels promote functional recovery after severe traumatic brain injury.J Neural Eng. 2024 Jun 27;21(3):036058. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad5108. J Neural Eng. 2024. PMID: 38806019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bishop JR; Schuksz M; Esko JD Heparan Sulphate Proteoglycans Fine-Tune Mammalian Physiology. Nature 2007, 446, 1030–1037. - PubMed
-
- Leu S-J; Chen N; Chen C-C; Todorović V; Bai T; Juric V; Liu Y; Yan G; Lam SC-T; Lau LF Targeted Mutagenesis of the Angiogenic Protein CCN1 (CYR61) Selective Inactivation of Integrin α6β1-Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Coreceptor-Mediated Cellular Functions. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 44177–44187. - PubMed
- Suarez SC; Pieren M; Cariolato L; Arn S; Hoffmann U; Bogucki A; Manlius C; Wood J; Ballmer-Hofer K A VEGF-A Splice Variant Defective for Heparan Sulfate and Neuropilin-1 Binding shows Attenuated Signaling through VEGFR-2. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2006, 63, 2067–2077. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi Y Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in the Nervous System: Their Diverse Roles in Neurogenesis, Axon Guidance, and Synaptogenesis. In Semin. Cell Dev. Biol, 2001; Elsevier: Vol. 12, pp. 99–106. - PubMed
-
- Ibrahimi OA; Zhang F; Hrstka SC; Mohammadi M; Linhardt RJ Kinetic model for FGF, FGFR, and proteoglycan signal transduction complex assembly. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 4724–4730. - PubMed
- Walker A; Turnbull JE; Gallagher JT Specific heparan sulfate saccharides mediate the activity of basic fibroblast growth factor. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 931–935. - PubMed
- Asada M; Shinomiya M; Suzuki M; Honda E; Sugimoto R; Ikekita M; Imamura T Glycosaminoglycan affinity of the complete fibroblast growth factor family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 40–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

