(1 → 3)-β-D-Glucan-guided antifungal therapy in adults with sepsis: the CandiSep randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 35708758
- PMCID: PMC9273538
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-022-06733-x
(1 → 3)-β-D-Glucan-guided antifungal therapy in adults with sepsis: the CandiSep randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate whether (1 → 3)-β-d-Glucan (BDG)-guidance shortens time to antifungal therapy and thereby reduces mortality of sepsis patients with high risk of invasive Candida infection (ICI).
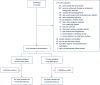
Methods: Multicenter, randomized, controlled trial carried out between September 2016 and September 2019 in 18 intensive care units enrolling adult sepsis patients at high risk for ICI. Patients in the control group received targeted antifungal therapy driven by culture results. In addition to targeted therapy, patients in the BDG group received antifungals if at least one of two consecutive BDG samples taken during the first two study days was ≥ 80 pg/mL. Empirical antifungal therapy was discouraged in both groups. The primary endpoint was 28-day-mortality.
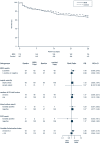
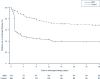
Results: 339 patients were enrolled. ICI was diagnosed in 48 patients (14.2%) within the first 96 h after enrollment. In the BDG-group, 48.8% (84/172) patients received antifungals during the first 96 h after enrollment and 6% (10/167) patients in the control group. Death until day 28 occurred in 58 of 172 patients (33.7%) in the BDG group and 51 of 167 patients (30.5%) in the control group (relative risk 1.10; 95% confidence interval, 0.80-1.51; p = 0.53). Median time to antifungal therapy was 1.1 [interquartile range (IQR) 1.0-2.2] days in the BDG group and 4.4 (IQR 2.0-9.1, p < 0.01) days in the control group.
Conclusions: Serum BDG guided antifungal treatment did not improve 28-day mortality among sepsis patients with risk factors for but unexpected low rate of IC. This study cannot comment on the potential benefit of BDG-guidance in a more selected at-risk population.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02734550.
Keywords: (1 → 3)-β-D-Glucan; Antifungal therapy; Biomarker; Invasive Candida infection; Sepsis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
FB received honoraria for an expert board meeting by Baxter. Prof. Cornely reports grants or contracts from Amplyx, Basilea, BMBF, Cidara, DZIF, EU-DG RTD (101037867), F2G, Gilead, Matinas, MedPace, MSD, Mundipharma, Octapharma, Pfizer, Scynexis; Consulting fees from Amplyx, Biocon, Biosys, Cidara, Da Volterra, Gilead, Matinas, MedPace, Menarini, Molecular Partners, MSG-ERC, Noxxon, Octapharma, PSI, Scynexis, Seres; Honoraria for lectures from Abbott, Al-Jazeera Pharmaceuticals, Astellas, Grupo Biotoscana/United Medical/Knight, Hikma, MedScape, MedUpdate, Merck/MSD, Mylan, Pfizer; Payment for expert testimony from Cidara; Participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board from Actelion, Allecra, Cidara, Entasis, IQVIA, Jannsen, MedPace, Paratek, PSI, Shionogi; A pending patent currently reviewed at the German Patent and Trade Mark Office; Other interests from DGHO, DGI, ECMM, ISHAM, MSG-ERC, Wiley. JH received grants and speaker honoraria from Pfizer, speaker honoraria from Gilead and consumables/test kits from Associates of Cape Cod. SK received research support from Cytosorbents and Daiichi Sankyo. He also received lecture fees from Astra, Bard, Baxter, Biotest, Cytosorbents, Daiichi Sankyo, Fresenius Medical Care, Gilead, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Pfizer, Philips and Zoll. He received consultant fees from Fresenius, Gilead, MSD and Pfizer. KK received honoraria for lecturing from Cytosorbents, Fresenius and Sedana. CP received lecture fees from Astra, C.R.Bard, Baxter, Biotest, Cytosorbents, Daiichi Sankyo, Fresenius, Gilead, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Pfizer, Philips and Zoll. He received consultant fees from Bayer, Fresenius, Gilead, MSD and Pfizer. He also received consultant fees from Messer, Pluristem, and Sedana and received lecture fees from Dräger Med. Inc. and Medronic. OM received honoraria for lectures during workshops on hemodynamic monitoring, supported by Pulsion (Maquet Critical Care) and for two lectures during industrial sessions at national congresses (HillRom, HepaWash); Unrestricted Research Grant from CSL Behring. DR has received support for attending meetings and/or travels from Gilead Sciences Inc., MSD, Pfizer. AW reported receiving honoraria for lecturing from Getinge and receiving personal fees from TEVA for consulting. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is (1,3)-β-D-glucan useless to guide antifungal therapy in ICU?Intensive Care Med. 2022 Jul;48(7):930-932. doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06766-2. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Intensive Care Med. 2022. PMID: 35771251 No abstract available.
References
-
- Koehler P, Stecher M, Cornely OA, et al. Morbidity and mortality of candidaemia in Europe: an epidemiologic meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;25:1200–1212. - PubMed
-
- Kollef M, Micek S, Hampton N, Doherty JA, Kumar A. Septic shock attributed to Candida infection: importance of empiric therapy and source control. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:1739–1746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

