The correlation between serum albumin and diabetic retinopathy among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: NHANES 2011-2020
- PMID: 35709212
- PMCID: PMC9202838
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270019
The correlation between serum albumin and diabetic retinopathy among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: NHANES 2011-2020
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this research aimed to investigate the correlation involving serum albumin with diabetic retinopathy (DR) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
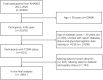
Methods: From 2011 to 2020, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) surveyed 45462 participants. We used the relevant data to conduct descriptive statistics, linear regression, and Logistic regression analysis.
Results: After adjusting for age, sex, and race, as well as all other variables, serum albumin was significantly negatively related to DR (P<0.001). Furthermore, after controlling for confounding factors, the third quartile (Q3) and the fourth quartile (Q4) had quite a negative significant relationship with the incidence of DR (P<0.01). The second quartile had a significant positive correlation with DR, whereas the observed negative correlations were not statistically meaningful (P>0.05).
Conclusion: Albumin levels in the serum have a quantitatively significant negative correlation with DR. Serum albumin levels in the blood can be used as a reference point for protracted follow-up of people with T2DM.
Conflict of interest statement
NO authors have competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2019;157: 107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Steinmetz JD, Bourne RRA, Briant PS, Flaxman SR, Taylor HRB, Jonas JB, et al. Causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: the Right to Sight: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. The Lancet Global Health. 2021;9: e144–e160. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30489-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical