Benefits of plasma exchange on mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35709964
- PMCID: PMC9192121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.014
Benefits of plasma exchange on mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
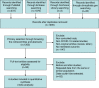
Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic continues, and the death toll continues to surge. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) on mortality in patients with COVID-19.
Methods: A systematic search was made of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and clinicaltrials.gov, without language restrictions. Controlled clinical trials on treatment of COVID-19 with TPE, compared with standard of care, were reviewed. Studies were pooled according to risk ratios (RRs) and weighted mean differences, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: A total of six trials (enrolling 343 participants) met the inclusion criteria. Therapeutic plasma exchange showed significant effect on mortality (RR 0.41, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.69; P = 0.0008).
Conclusion: TPE significantly reduced mortality in hospitalized patients with moderate-to-critical COVID-19. Plasma exchange therapy should be considered for patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Meta-analysis; Mortality; Plasma exchange.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

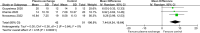
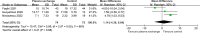
Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 May;20(4):931-937. doi: 10.1007/s12015-024-10705-7. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 38427315
-
Pregabalin add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 29;3(3):CD005612. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005612.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35349176 Free PMC article.
-
Colchicine for the treatment of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 18;10(10):CD015045. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015045. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34658014 Free PMC article.
-
Negative pressure wound therapy for surgical wounds healing by primary closure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 26;4(4):CD009261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009261.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35471497 Free PMC article.
-
Nirmatrelvir combined with ritonavir for preventing and treating COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 20;9(9):CD015395. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015395.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 30;11:CD015395. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015395.pub3. PMID: 36126225 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Benefits of ozone on mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Complement Ther Med. 2023 Mar;72:102907. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2022.102907. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Complement Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 36513208 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of tolvaptan on early dyspnea relief in patients with acute heart failure: A meta-analysis.Clin Cardiol. 2022 Oct;45(10):995-1001. doi: 10.1002/clc.23889. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Clin Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35916355 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Survival in Septic Shock: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Plasma Exchange Therapy.Cureus. 2024 May 23;16(5):e60947. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60947. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38910774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral sepsis: diagnosis, clinical features, pathogenesis, and clinical considerations.Mil Med Res. 2024 Dec 16;11(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00581-0. Mil Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39676169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma (CCP) During the Pandemic Era: A Literature Review.J Blood Med. 2023 Feb 22;14:159-187. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S397722. eCollection 2023. J Blood Med. 2023. PMID: 36855559 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Busund R, Koukline V, Utrobin U, Nedashkovsky E. Plasmapheresis in severe sepsis and septic shock: a prospective, randomised, controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2002;28:1434–1439. - PubMed
-
- Detsky AS, Naylor CD, O'Rourke K, McGeer AJ, L'Abbé KA. Incorporating variations in the quality of individual randomized trials into meta-analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45:255–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

