Viral load monitoring for people living with HIV in the era of test and treat: progress made and challenges ahead - a systematic review
- PMID: 35710413
- PMCID: PMC9202111
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-022-13504-2
Viral load monitoring for people living with HIV in the era of test and treat: progress made and challenges ahead - a systematic review
Abstract
Background: In 2016, we conducted a systematic review to assess the feasibility of treatment monitoring for people living with HIV (PLHIV) receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) in low and middle-income countries (LMICs), in line with the 90-90-90 treatment target. By 2020, global estimates suggest the 90-90-90 target, particularly the last 90, remains unattainable in many LMICs. This study aims to review the progress and identify needs for public health interventions to improve viral load monitoring and viral suppression for PLHIV in LMICs.
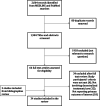
Methods: A literature search was conducted using an update of the initial search strategy developed for the 2016 review. Electronic databases (Medline and PubMed) were searched to identify relevant literature published in English between Dec 2015 and August 2021. The primary outcome was initial viral load (VL) monitoring (the proportion of PLHIV on ART and eligible for VL monitoring who received a VL test). Secondary outcomes included follow-up VL monitoring (the proportion of PLHIV who received a follow-up VL after an initial elevated VL test), confirmation of treatment failure (the proportion of PLHIV who had two consecutive elevated VL results) and switching treatment regimen rates (the proportion of PLHIV who switched treatment regimen after confirmation of treatment failure).
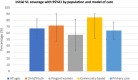
Results: The search strategy identified 1984 non-duplicate records, of which 34 studies were included in the review. Marked variations in initial VL monitoring coverage were reported across study settings/countries (range: 12-93% median: 74% IQR: 46-82%) and study populations (adults (range: 25-96%, median: 67% IQR: 50-84%), children, adolescents/young people (range: 2-94%, median: 72% IQR: 47-85%), and pregnant women (range: 32-82%, median: 57% IQR: 43-71%)). Community-based models reported higher VL monitoring (median: 85%, IQR: 82-88%) compared to decentralised care at primary health facility (median: 64%, IRQ: 48-82%). Suboptimal uptake of follow-up VL monitoring and low regimen switching rates were observed.
Conclusions: Substantial gaps in VL coverage across study settings and study populations were evident, with limited data availability outside of sub-Saharan Africa. Further research is needed to fill the data gaps. Development and implementation of innovative, community-based interventions are required to improve VL monitoring and address the "failure cascade" in PLHIV on ART who fail to achieve viral suppression.
Keywords: Decentralisation; HIV; Low and middle-income countries; Viral load monitoring.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS, 90-90-90: an ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. 2014, Joint United Nations Progamme on HIV/AIDS: Geneva, Switzeland. Available at https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2017/90-90-90. Accessed 14 July 2020.
-
- Quinn TC, et al. Viral load and heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Rakai Project Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(13):921–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials