Transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.214 and Alpha Variants during 4 COVID-19 Waves, Kyoto, Japan, January 2020-June 2021
- PMID: 35710464
- PMCID: PMC9328921
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2808.220420
Transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.214 and Alpha Variants during 4 COVID-19 Waves, Kyoto, Japan, January 2020-June 2021
Abstract
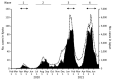
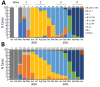
Household transmission is a primary source of SARS-CoV-2 spread. We used COVID-19 epidemiologic investigation data and viral genome analysis data collected in the city of Kyoto, Japan, during January 2020-June 2021 to evaluate the effects of different settings and viral strains on SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Epidemiologic investigations of 5,061 COVID-19 cases found that the most common category for close contact was within households (35.3%); this category also had the highest reverse transcription PCR positivity. The prevalent viral lineage shifted from B.1.1.214 in the third wave to the Alpha variant in the fourth wave. The proportion of secondary cases associated with households also increased from the third to fourth waves (27% vs. 29%). Among 564 contacts from 206 households, Alpha variant was significantly associated with household transmission (odds ratio 1.52, 95% CI 1.06-2.18) compared with B.1.1.214. Public health interventions targeting household contacts and specific variants could help control SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
Keywords: COVID-19; Japan; SARS; SARS-CoV-2; contact tracing; coronavirus; coronavirus disease; epidemiology; household contact; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viral genome; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Contact tracing in the context of COVID-19: interim guidance, 1 February 2021. [cited 2022 Feb 21]. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/339128
-
- Oshitani H; Expert Members of The National COVID-19 Cluster Taskforce at The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan. Cluster-based approach to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) response in Japan, from February to April 2020. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2020;73:491–3. 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2020.363 - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Report of the WHO–China joint mission on coronavirus disease 2019. (COVID-19) [cited 2022 Feb 21]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/report-of-the-who-china-joint-mi...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

