Genome-wide association study of musical beat synchronization demonstrates high polygenicity
- PMID: 35710621
- PMCID: PMC9489530
- DOI: 10.1038/s41562-022-01359-x
Genome-wide association study of musical beat synchronization demonstrates high polygenicity
Abstract
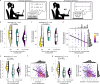
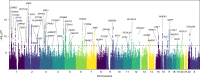
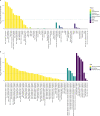
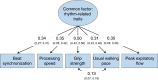
Moving in synchrony to the beat is a fundamental component of musicality. Here we conducted a genome-wide association study to identify common genetic variants associated with beat synchronization in 606,825 individuals. Beat synchronization exhibited a highly polygenic architecture, with 69 loci reaching genome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10-8) and single-nucleotide-polymorphism-based heritability (on the liability scale) of 13%-16%. Heritability was enriched for genes expressed in brain tissues and for fetal and adult brain-specific gene regulatory elements, underscoring the role of central-nervous-system-expressed genes linked to the genetic basis of the trait. We performed validations of the self-report phenotype (through separate experiments) and of the genome-wide association study (polygenic scores for beat synchronization were associated with patients algorithmically classified as musicians in medical records of a separate biobank). Genetic correlations with breathing function, motor function, processing speed and chronotype suggest shared genetic architecture with beat synchronization and provide avenues for new phenotypic and genetic explorations.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.F.S., D.A.H. and members of the 23andMe Research Team are employees of 23andMe, Inc., and hold stock or stock options in 23andMe. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ravignani, A., Delgado, T. & Kirby, S. Musical evolution in the lab exhibits rhythmic universals. Nat. Hum. Behav.10.1038/s41562-016-0007 (2017).
-
- Kotz, S. A., Ravignani, A. & Fitch, W. T. The evolution of rhythm processing. Trends Cogn. Sci.10.1016/j.tics.2018.08.002 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC016977/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025141/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD074711/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115305/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K18 DC017383/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM127087/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 HD098859/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM152284/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103537/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032830/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

