RUNX3-regulated circRNA METTL3 inhibits colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis via miR-107/PER3 axis
- PMID: 35710754
- PMCID: PMC9203801
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-04750-8
RUNX3-regulated circRNA METTL3 inhibits colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis via miR-107/PER3 axis
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: RUNX3-regulated circRNA METTL3 inhibits colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis via miR-107/PER3 axis.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 7;15(2):117. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06497-w. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38326300 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
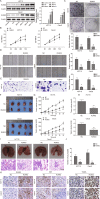
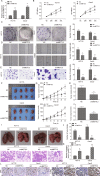
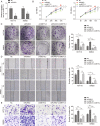
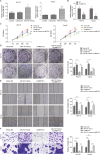
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most prevalent and lethal malignancies. Exploring the underlying molecular mechanisms is very helpful for the development of new therapy. Here, we investigated the function of circMETTL3/miR-107/PER3 in CRC. Human CRC tissues from diagnosed CRC patients and six CRC cell lines, one normal human colon cell line were used. qRT-PCR and western blotting were performed to determine expression levels of RUNX3, circMETTL3, miR-107, PER3, and proliferation-, and migration-related proteins. CCK-8, colony formation assay, transwell assay, and scratch wound assay were utilized to assess CRC cell proliferation and invasion. ChIP, EMSA, biotin-pull down, RIP assay, and dual luciferase reporter assay were performed to validate interactions of RUNX3/METTL3 promoter, circMETTL3/miR-107, and miR-107/PER3. FISH was used to characterize circMETTL3. MSP was employed to measure methylation level. Nude mouse xenograft model was used to determine the effects on tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. RUNX3, circMETTL3, and PER3 were diminished while miR-107 was elevated in CRC tissues and cells. Low levels of RUNX3 and circMETTL3 correlated with poor prognosis of CRC. Overexpression of RUNX3, circMETTL3, or PER3 suppressed while miR-107 mimics promoted, CRC cell proliferation and invasion, as well as tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, RUNX3 bound to METTL3 promoter and activated circMETTL3 transcription. circMETTL3 directly bound with miR-107 which targeted PER3. circMETTL3/miR-107 regulated CRC cell proliferation and invasion via PER3. CircMETTL3, transcriptionally activated by RUNX3, restrains CRC development and metastasis via acting as a miR-107 sponge to regulate PER3 signaling.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

