Genome-wide polygenic score to predict chronic kidney disease across ancestries
- PMID: 35710995
- PMCID: PMC9329233
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01869-1
Genome-wide polygenic score to predict chronic kidney disease across ancestries
Abstract
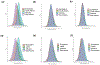
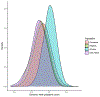
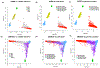
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common complex condition associated with high morbidity and mortality. Polygenic prediction could enhance CKD screening and prevention; however, this approach has not been optimized for ancestrally diverse populations. By combining APOL1 risk genotypes with genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of kidney function, we designed, optimized and validated a genome-wide polygenic score (GPS) for CKD. The new GPS was tested in 15 independent cohorts, including 3 cohorts of European ancestry (n = 97,050), 6 cohorts of African ancestry (n = 14,544), 4 cohorts of Asian ancestry (n = 8,625) and 2 admixed Latinx cohorts (n = 3,625). We demonstrated score transferability with reproducible performance across all tested cohorts. The top 2% of the GPS was associated with nearly threefold increased risk of CKD across ancestries. In African ancestry cohorts, the APOL1 risk genotype and polygenic component of the GPS had additive effects on the risk of CKD.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors declare no existing competing interest.
Figures

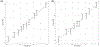

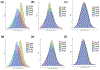
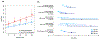
Comment in
-
A polygenic score predicts CKD across ancestries.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022 Nov;18(11):681-682. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00622-8. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35953653 No abstract available.
-
Including APOL1 alleles and ancestry adjustments improve a genome-wide polygenic CKD score.Kidney Int. 2022 Nov;102(5):954-955. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.004. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 35985372 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Chronic kidney disease: highlights from research.Nature. 2023 Mar;615(7951):S16-S17. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-00655-4. Nature. 2023. PMID: 36890364 No abstract available.
References
-
- Coresh J, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. Jama-J Am Med Assoc 298, 2038–2047 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States, (n.d.). https://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/publications-resources/ckd-national-fa... (accessed February 21, 2022).
-
- Fox CS, et al. Genomewide linkage analysis to serum creatinine, GFR, and creatinine clearance in a community-based population: the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Soc Nephrol 15, 2457–2461 (2004). - PubMed
Methods References:
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 DK128990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG054573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011167/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK116672/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK116967/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL133373/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM140487/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS041588/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD043483/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 DK114926/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055673/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM013061/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL123782/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 DK128563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136666/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008680/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011176/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL155466/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151855/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008685/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DK116690/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

