Effects of short-term food deprivation on catecholamine and metabolic-sensory biomarker gene expression in hindbrain A2 noradrenergic neurons projecting to the forebrain rostral preoptic area: Impact of negative versus positive estradiol feedback
- PMID: 35711244
- PMCID: PMC9193863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.06.001
Effects of short-term food deprivation on catecholamine and metabolic-sensory biomarker gene expression in hindbrain A2 noradrenergic neurons projecting to the forebrain rostral preoptic area: Impact of negative versus positive estradiol feedback
Abstract
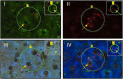
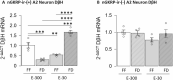
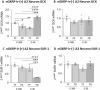
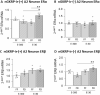
Hindbrain A2 noradrenergic neurons assimilate estrogenic and metabolic cues. In female mammals, negative- versus positive-feedback patterns of estradiol (E) secretion impose divergent regulation of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) neuroendocrine axis. Current research used retrograde tracing, dual-label immunocytochemistry, single-cell laser-microdissection, and multiplex qPCR methods to address the premise that E feedback modes uniquely affect metabolic regulation of A2 neurons involved in HPG control. Ovariectomized female rats were given E replacement to replicate plasma hormone levels characteristic of positive (high-E dose) or negative (low-E dose) feedback. Animals were either full-fed (FF) or subjected to short-term, e.g., 18-h food deprivation (FD). After FF or FD, rostral preoptic area (rPO)-projecting A2 neurons were characterized by the presence or absence of nuclear glucokinase regulatory protein (nGKRP) immunostaining. FD augmented or suppressed mRNAs encoding the catecholamine enzyme dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DβH) and the metabolic-sensory biomarker glucokinase (GCK), relative to FF controls, in nGKRP-immunoreactive (ir)-positive A2 neurons from low-E or high-E animals, respectively. Yet, these transcript profiles were unaffected by FD in nGKRP-ir-negative A2 neurons at either E dosage level. FD altered estrogen receptor (ER)-alpha and ATP-sensitive potassium channel subunit sulfonylurea receptor-1 gene expression in nGKRP-ir-positive neurons from low-E, but not high-E animals. Results provide novel evidence that distinct hindbrain A2 neuron populations exhibit altered versus unaffected transmission to the rPO during FD-associated metabolic imbalance, and that the direction of change in this noradrenergic input is controlled by E feedback mode. These A2 cell types are correspondingly distinguished by FD-sensitive or -insensitive GCK, which correlates with the presence versus absence of nGKRP-ir. Further studies are needed to determine how E signal volume regulates neurotransmitter and metabolic sensor responses to FD in GKRP-expressing A2 neurons.
Keywords: AMPK, adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase; DVC, dorsal vagal complex; Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase; DβH, dopamine-beta-hydroxylase; E, estradiol; ERα, estrogen receptor-alpha; ERβ, estrogen receptor-beta; Estradiol; FD, food-deprivation; FF, full-fed; Food deprivation; GCK, glucokinase; GKRP, glucokinase regulatory protein; Glucokinase; Glucokinase regulatory protein; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; HPG, hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal; KATP, ATP-sensitive potassium channel; LH, luteinizing hormone; NE, norepinephrine; O.D., optical density; OVX, ovariectomy; SUR-1, sulfonylurea receptor-1; Single-cell quantitative multiplex PCR; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; pAMPK, phospho-AMPK; rPO, rostral preoptic area.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Adler, B.A., Johnson, M.D., Lynch, C.O., Crowley, W.R. Evidence that norepinephrine and epinephrine systems mediate the stimulatory effects of ovarian hormones on luteinizing hormone and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. - PubMed
-
- Alshamrani A., Bheemanapally K., Ibrahim M.M.H., Briski K.P. Impact of caudal hindbrain glycogen metabolism on A2 noradrenergic neuron AMPK activation and ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus norepinephrine activity and glucoregulatory neuro-transmitter marker protein expression. Neuropeptides. 2020;82 - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
