COVID-19 and Preexisting Comorbidities: Risks, Synergies, and Clinical Outcomes
- PMID: 35711466
- PMCID: PMC9196863
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.890517
COVID-19 and Preexisting Comorbidities: Risks, Synergies, and Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
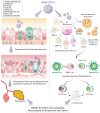
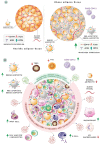
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and its associated symptoms, named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), have rapidly spread worldwide, resulting in the declaration of a pandemic. When several countries began enacting quarantine and lockdown policies, the pandemic as it is now known truly began. While most patients have minimal symptoms, approximately 20% of verified subjects are suffering from serious medical consequences. Co-existing diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and others, have been shown to make patients more vulnerable to severe outcomes from COVID-19 by modulating host-viral interactions and immune responses, causing severe infection and mortality. In this review, we outline the putative signaling pathways at the interface of COVID-19 and several diseases, emphasizing the clinical and molecular implications of concurring diseases in COVID-19 clinical outcomes. As evidence is limited on co-existing diseases and COVID-19, most findings are preliminary, and further research is required for optimal management of patients with comorbidities.
Keywords: COVID-19; cancer; cardiovascular disease; coronavirus disease 2019; diabetes; immune responses; treatment implications.
Copyright © 2022 Bigdelou, Sepand, Najafikhoshnoo, Negrete, Sharaf, Ho, Sullivan, Chauhan, Etter, Shekarian, Liang, Hutter, Esfandiarpour and Zanganeh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

