Effect of DL-Methylephedrine on Dopamine Transporter Using Positron Emission Tomography With [18F]FE-PE2I
- PMID: 35711596
- PMCID: PMC9193582
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.799319
Effect of DL-Methylephedrine on Dopamine Transporter Using Positron Emission Tomography With [18F]FE-PE2I
Abstract
Rationale: Since ephedrine has a dopamine transporter (DAT) inhibitory effect similar to amphetamine, dl-methylephedrine, a derivative of ephedrine, is considered to have the characteristics of a central nervous system stimulant due to the DAT inhibitory effect. For example, the World Anti-Doping Agency categorizes dl-methylephedrine as a stimulant in the prohibited list for competitions. Assuming to have the same effect as ephedrine, the urinary concentration of dl-methylephedrine is regulated below 10 μg/mL, as is ephedrine. However, the extent to which dl-methylephedrine affects brain function is not yet fully understood.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to evaluate DAT occupancy by a single oral administration of a daily dose of dl-methylephedrine using positron emission tomography (PET) with [18F]FE-PE2I to characterize its stimulatory effect on the central nervous system.
Methods: Nine healthy male volunteers were enrolled in the study. The experiments were designed as a placebo-controlled randomized double-blind crossover comparative study. After the first PET scan in a drug-free state, the second and third PET scans were performed with randomized dosing at 60 mg of dl-methylephedrine or placebo. The plasma and urine concentrations of dl-methylephedrine were measured just before and after the PET scans, respectively.
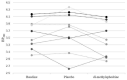
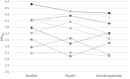
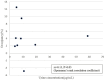
Results: Mean urine and plasma concentrations of dl-methylephedrine were 13.9 μg/mL and 215.2 ng/mL, respectively. Mean DAT occupancy in the caudate was 4.4% for dl-methylephedrine and 1.2% for placebo. Mean DAT occupancy in the putamen was 3.6% for dl-methylephedrine and 0.5% for placebo. There was no significant difference of DAT occupancies between the groups.
Conclusion: In this study, the urinary concentration of dl-methylephedrine (13.9 μg/mL) was higher than the prohibited reference value (10.0 μg/mL), and there was no significant difference in DAT occupancy between dl-methylephedrine and placebo. These findings suggest that a clinical daily dose of dl-methylephedrine may exceed the doping regulation value according to urine concentration; however, it was considered that at least the central excitatory effect mediated by DAT inhibition was not observed at the daily dose of dl-methylephedrine.
Keywords: [18F]FE-PE2I; dl-methylephedrine; dopamine transporter; doping; positron emission tomography.
Copyright © 2022 Nogami, Arakawa, Sakayori, Ikeda, Okubo and Tateno.
Conflict of interest statement
RA has received speaker's honoraria from Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Meiji, Pfizer. YO has received grants or speaker's honoraria from Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Astellas, Yoshitomi and Meiji. AT has received speaker's honoraria from Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical within past 3 years. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

