Chiral Separation of Stilbene Dimers Generated by Biotransformation for Absolute Configuration Determination and Antibacterial Evaluation
- PMID: 35711965
- PMCID: PMC9194554
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.912396
Chiral Separation of Stilbene Dimers Generated by Biotransformation for Absolute Configuration Determination and Antibacterial Evaluation
Abstract
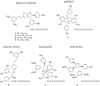
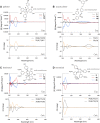
A series of complex stilbene dimers have been generated through biotransformation of resveratrol, pterostilbene, and the mixture of both using the enzymatic secretome of Botrytis cinerea Pers. The process starts with achiral molecules and results in the generation of complex molecules with multiple chiral carbons. So far, we have been studying these compounds in the form of enantiomeric mixtures. In the present study, we isolated the enantiomers to determine their absolute configuration and assess if the stereochemistry could impact their biological properties. Eight compounds were selected for this study, corresponding to the main scaffolds generated (pallidol, leachianol, restrytisol and acyclic dimers) and the most active compounds (trans-δ-viniferin derivatives) against a methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). To isolate these enantiomers and determine their absolute configuration, a chiral HPLC-PDA analysis was performed. The analysis was achieved on a high-performance liquid chromatography system equipped with a chiral column. For each compound, the corresponding enantiomeric pair was obtained with high purity. The absolute configuration of each enantiomer was determined by comparison of experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism (ECD). The antibacterial activities of the four trans-δ-viniferin derivatives against two S. aureus strains were evaluated.
Keywords: Botrytis cinerea Pers.; ECD calculations; MRSA; Staphylococcus aureus; biotransformation; chiral-HPLC; enantiomers; stilbene dimers.
Copyright © 2022 Huber, Marcourt, Quiros-Guerrero, Luscher, Schnee, Michellod, Ducret, Kohler, Perron, Wolfender, Gindro and Ferreira Queiroz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bhusainahalli V. M., Spatafora C., Chalal M., Vervandier-Fasseur D., Meunier P., Latruffe N., et al. (2012). Resveratrol-related Dehydrodimers: Laccase-Mediated Biomimetic Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 5217–5224. 10.1002/ejoc.201200664 - DOI
-
- Gavezzotti P., Bertacchi F., Fronza G., Křen V., Monti D., Riva S. (2015). Laccase-catalyzed Dimerization of Piceid, a Resveratrol Glucoside, and its Further Enzymatic Elaboration. Adv. Synth. Catal. 357, 1831–1839. 10.1002/adsc.201500185 - DOI
-
- Huber R., Koval A., Marcourt L., Héritier M., Schnee S., Michellod E., et al. (2022). Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Original Stilbene Dimers Possessing Wnt Inhibition Activity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Using the Enzymatic Secretome of Botrytis cinerea Pers. Front. Chem. 10, 881298. 10.3389/fchem.2022.881298 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

