Beyond QuantiFERON-TB Results, the Added Value of a Weak Mitogen Response
- PMID: 35712107
- PMCID: PMC9197320
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.876864
Beyond QuantiFERON-TB Results, the Added Value of a Weak Mitogen Response
Abstract
Introduction: While QuantiFERON-TB gold (QFT) is frequently used, little attention is paid to the mitogen response. How it could be impacted and associated with outcomes is poorly known.
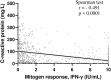
Methods: Retrospective, case-control study in hospitalized patients who underwent QFT testing in two hospitals between 2016 and 2019. We defined two groups of cases with either negative [interferon (IFN)-γ ≤ 0.5 IU/ml, official threshold] or weak (0.5-2 IU/ml) mitogen response, and one group of controls with normal (>2 IU/ml) mitogen response.
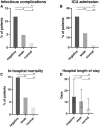
Results: A total of 872 patients were included. An ongoing infection was independently associated with both a negative (RR = 4.34; 95% CI = 2.94-6.41) and a weak mitogen response (RR = 2.44; 95% CI = 1.66-3.58). Among tuberculosis patients, a weak mitogen response was associated with a false-negative QFT result (75%) compared to a normal response (20%). Decreasing mitogen response (normal, weak and negative, respectively) was associated with increasing length of hospital stay [median (interquartile range) 5 (3-13), 11 (5-21) and 15 (10-30) days; p < 0.001] and increasing hospital mortality (3, 7, and 15%; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Clinicians should take notice of the mitogen response since IFN-γ concentrations lower than <2 IU/ml were associated with false-negative QFT results in tuberculosis patients, independently associated with ongoing infections, and could be associated with worse prognosis.
Keywords: QuantiFERON; infection; mitogen; mortality; outcomes.
Copyright © 2022 Jacquier, Binquet, Manoha, Audia, Simonet-Lamm, Casenaz, Sow, Piroth and Blot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lange B, Vavra M, Kern WV, Wagner D. Indeterminate results of a tuberculosis-specific interferon- release assay in immunocompromised patients. Eur Respir J. (2010) 35:1179-82. - PubMed
-
- Hradsky O, Ohem J, Zarubova K, Mitrova K, Durilova M, Kotalova R, et al. Disease activity is an important factor for indeterminate interferon-γ release assay results in children with inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutrit. (2014) 58:320-4. 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000205 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

