Long-Term Study of Relapse After Mandibular Orthognathic Surgery: Advancement Versus Setback
- PMID: 35712437
- PMCID: PMC9192893
- DOI: 10.1007/s12663-020-01445-5
Long-Term Study of Relapse After Mandibular Orthognathic Surgery: Advancement Versus Setback
Abstract
Background: Relapse is a continuing process and should be evaluated on a long rather than short term.
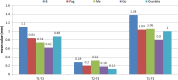
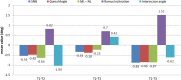
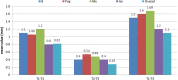
Materials and methods: Treatment records of 46 patients who underwent mandibular orthognathic surgery were divided into two groups, i.e. Group 1: Mandibular Advancement (MA) surgery (n = 26) and Group 2: Mandibular Setback (MS) surgery (n = 20). Lateral cephalograms were traced at T0 (01 week before surgery), T1 (01 week after surgery), T2 (01 year after surgery) and T3 (minimum 05 years after surgery) to study short- and long-term skeletal and dental relapse in horizontal, vertical and angular parameters selected for the study. Relapse was correlated with gender, age, amount of surgical movement and intra-operative change in mandibular plane angle to study effect of these factors on relapse.
Results: All horizontal, vertical and angular parameters studied showed significant relapse at short term (from T1 to T2) which continued significantly till long-term evaluation (T2 to T3) in both groups (P value < 0.001). Horizontal relapse in all parameters, vertical relapse in all parameters (except Pog and overbite at T1-T2) and angular relapse in all parameters (except Ramus inclination at T1-T2) was significantly higher in Group 2 compared to Group 1 (P value < 0.001 for all). Relapse showed significant and positive correlation with amount of surgical movement and intra-operative change in mandibular plane angle in both groups (P value < 0.05 for all).
Conclusion: Both MA and MS surgeries show significant relapse on both short- and long-term evaluation which it is higher in MS as compared to MA surgeries.
Keywords: Advancement surgery; Long-term relapse; Mandibular orthognathic surgery; Setback surgery.
© The Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons of India 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
