β-Boswellic Acid Suppresses Breast Precancerous Lesions via GLUT1 Targeting-Mediated Glycolysis Inhibition and AMPK Pathway Activation
- PMID: 35712503
- PMCID: PMC9194511
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.896904
β-Boswellic Acid Suppresses Breast Precancerous Lesions via GLUT1 Targeting-Mediated Glycolysis Inhibition and AMPK Pathway Activation
Abstract
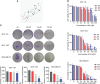
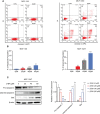
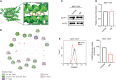
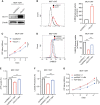
Breast carcinoma is a multistep progressive disease. Precancerous prevention seems to be crucial. β-Boswellic acid (β-BA), the main component of the folk medicine Boswellia serrata (B. serrata), has been reported to be effective in various diseases including tumors. In this work, we demonstrated that β-BA could inhibit breast precancerous lesions in rat disease models. Consistently, β-BA could suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis on MCF-10AT without significantly influencing MCF-10A. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis suggested that β-BA may interfere with the metabolic pathway. Metabolism-related assays showed that β-BA suppressed glycolysis and reduced ATP production, which then activated the AMPK pathway and inhibited the mTOR pathway to limit MCF-10AT proliferation. Further molecular docking analysis suggested that GLUT1 might be the target of β-BA. Forced expression of GLUT1 could rescue the glycolysis suppression and survival limitation induced by β-BA on MCF-10AT. Taken together, β-BA could relieve precancerous lesions in vivo and in vitro through GLUT1 targeting-induced glycolysis suppression and AMPK/mTOR pathway alterations. Here, we offered a molecular basis for β-BA to be developed as a promising drug candidate for the prevention of breast precancerous lesions.
Keywords: AMPK; GLUT1; breast precancerous lesions; glycolysis; β-boswellic acid.
Copyright © 2022 Bie, Zhang, Yan, Ma, Zhan, Qiu, Cao, Ma and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic Acid Inhibits Precancerous Breast Lesion MCF-10AT Cells via Regulation of LINC00707/miR-206 that Reduces Estrogen Receptor-α.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Mar 27;12:2301-2314. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S238051. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32273767 Free PMC article.
-
Boswellic acids trigger apoptosis via a pathway dependent on caspase-8 activation but independent on Fas/Fas ligand interaction in colon cancer HT-29 cells.Carcinogenesis. 2002 Dec;23(12):2087-93. doi: 10.1093/carcin/23.12.2087. Carcinogenesis. 2002. PMID: 12507932
-
Betulinic acid suppresses breast cancer aerobic glycolysis via caveolin-1/NF-κB/c-Myc pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;161:149-162. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.01.016. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30684465
-
Pharmacological evidences for cytotoxic and antitumor properties of Boswellic acids from Boswellia serrata.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;191:315-323. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.053. Epub 2016 Jun 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27346540 Review.
-
Boswellic acids/Boswellia serrata extract as a potential COVID-19 therapeutic agent in the elderly.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Aug;29(4):1033-1048. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00841-8. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34224069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-cancer properties of boswellic acids: mechanism of action as anti-cancerous agent.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 3;14:1187181. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1187181. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37601048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pepsin enhances glycolysis to promote malignant transformation of vocal fold leukoplakia epithelial cells with dysplasia.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Apr;280(4):1841-1854. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07729-5. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36380093 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Properties of Frankincense: Implications for Anticancer Therapy.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Aug;30(8):759-767. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-4105-x. Epub 2024 May 31. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38816637
References
-
- O’Shaughnessy JA, Kelloff GJ, Gordon GB, Dannenberg AJ, Hong WK, Fabian CJ, et al. . Treatment and Prevention of Intraepithelial Neoplasia: An Important Target for Accelerated New Agent Development - Recommendations of the American Association for Cancer Research Task Force on the Treatment and Prevention of Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Clin Cancer Res (2002) 8(2):314–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

