Extensively drug-resistant (XDR) Neisseria gonorrhoeae causing possible gonorrhoea treatment failure with ceftriaxone plus azithromycin in Austria, April 2022
- PMID: 35713023
- PMCID: PMC9205165
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.24.2200455
Extensively drug-resistant (XDR) Neisseria gonorrhoeae causing possible gonorrhoea treatment failure with ceftriaxone plus azithromycin in Austria, April 2022
Abstract
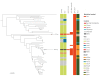
We describe a gonorrhoea case with ceftriaxone plus high-level azithromycin resistance. In April 2022, an Austrian heterosexual male was diagnosed with gonorrhoea after sexual intercourse with a female sex worker in Cambodia. Recommended treatment with ceftriaxone (1 g) plus azithromycin (1.5 g) possibly failed. Worryingly, this is the second strain in an Asian Neisseria gonorrhoeae genomic sublineage including high-level azithromycin-resistant strains that developed ceftriaxone resistance by acquisition of mosaic penA-60.001. Enhanced resistance surveillance and actions are imperative to prevent spread.
Keywords: Neisseria gonorrhoeae; XDR; ceftriaxone resistance; extensively drug-resistant; high-level azithromycin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO guidelines for the treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Geneva: WHO; 2016. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549691 - PubMed
-
- Cole MJ, Day M, Jacobsson S, Amato-Gauci AJ, Spiteri G, Unemo M, the European Gonorrhoea Response Plan Group. European Gonorrhoea Response Plan Group . The European response to control and manage multi- and extensively drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Euro Surveill. 2022;27(18). 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.18.2100611 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous