Loss of Elp1 disrupts trigeminal ganglion neurodevelopment in a model of familial dysautonomia
- PMID: 35713404
- PMCID: PMC9273214
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.71455
Loss of Elp1 disrupts trigeminal ganglion neurodevelopment in a model of familial dysautonomia
Abstract
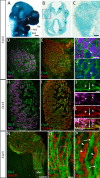
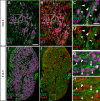
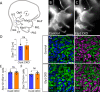
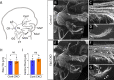
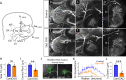
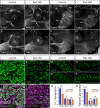
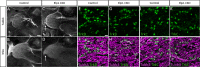
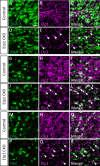
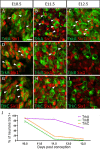
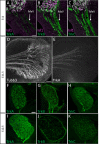
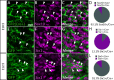
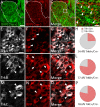
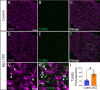
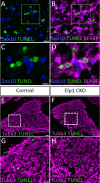
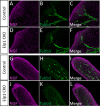
Familial dysautonomia (FD) is a sensory and autonomic neuropathy caused by mutations in elongator complex protein 1 (ELP1). FD patients have small trigeminal nerves and impaired facial pain and temperature perception. These signals are relayed by nociceptive neurons in the trigeminal ganglion, a structure that is composed of both neural crest- and placode-derived cells. Mice lacking Elp1 in neural crest derivatives ('Elp1 CKO') are born with small trigeminal ganglia, suggesting Elp1 is important for trigeminal ganglion development, yet the function of Elp1 in this context is unknown. We demonstrate that Elp1, expressed in both neural crest- and placode-derived neurons, is not required for initial trigeminal ganglion formation. However, Elp1 CKO trigeminal neurons exhibit abnormal axon outgrowth and deficient target innervation. Developing nociceptors expressing the receptor TrkA undergo early apoptosis in Elp1 CKO, while TrkB- and TrkC-expressing neurons are spared, indicating Elp1 supports the target innervation and survival of trigeminal nociceptors. Furthermore, we demonstrate that specific TrkA deficits in the Elp1 CKO trigeminal ganglion reflect the neural crest lineage of most TrkA neurons versus the placodal lineage of most TrkB and TrkC neurons. Altogether, these findings explain defects in cranial gangliogenesis that may lead to loss of facial pain and temperature sensation in FD.
Keywords: developmental biology; familial dysautonomia; mouse; neural crest cells; placode cells; trigeminal ganglion; trigeminal nerves; trks.
© 2022, Leonard et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CL, JQ, LT No competing interests declared, FL is the Co-Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board of the Familial Dysautonomia Foundation, Inc
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elp1 function in placode-derived neurons is critical for proper trigeminal ganglion development.Dev Dyn. 2025 Jun;254(6):494-512. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.749. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Dev Dyn. 2025. PMID: 39381860 Free PMC article.
-
Elp1 function in placode-derived neurons is critical for proper trigeminal ganglion development.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 16:2024.07.12.603323. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.12.603323. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Dev Dyn. 2025 Jun;254(6):494-512. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.749. PMID: 39071383 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A neuron autonomous role for the familial dysautonomia gene ELP1 in sympathetic and sensory target tissue innervation.Development. 2014 Jun;141(12):2452-61. doi: 10.1242/dev.107797. Development. 2014. PMID: 24917501 Free PMC article.
-
Animal and cellular models of familial dysautonomia.Clin Auton Res. 2017 Aug;27(4):235-243. doi: 10.1007/s10286-017-0438-2. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Clin Auton Res. 2017. PMID: 28667575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Familial dysautonomia.Clin Auton Res. 2023 Jun;33(3):269-280. doi: 10.1007/s10286-023-00941-1. Epub 2023 May 19. Clin Auton Res. 2023. PMID: 37204536 Review.
Cited by
-
The transcriptional landscape of the developing chick trigeminal ganglion.Dev Biol. 2025 Apr;520:108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2024.12.013. Epub 2024 Dec 22. Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39719193
-
Transcriptome analysis in a humanized mouse model of familial dysautonomia reveals tissue-specific gene expression disruption in the peripheral nervous system.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 4;14(1):570. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-51137-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38177237 Free PMC article.
-
ELP1, the Gene Mutated in Familial Dysautonomia, Is Required for Normal Enteric Nervous System Development and Maintenance and for Gut Epithelium Homeostasis.J Neurosci. 2024 Sep 11;44(37):e2253232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2253-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39138000 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Meis2 controls whisker development independently from trigeminal sensory innervation.Elife. 2025 Apr 4;13:RP100854. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100854. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40183774 Free PMC article.
-
Elp1 function in placode-derived neurons is critical for proper trigeminal ganglion development.Dev Dyn. 2025 Jun;254(6):494-512. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.749. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Dev Dyn. 2025. PMID: 39381860 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

