Hidden codes in mRNA: Control of gene expression by m6A
- PMID: 35714585
- PMCID: PMC9216239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.029
Hidden codes in mRNA: Control of gene expression by m6A
Abstract
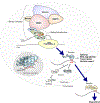
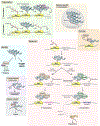
Information in mRNA has largely been thought to be confined to its nucleotide sequence. However, the advent of mapping techniques to detect modified nucleotides has revealed that mRNA contains additional information in the form of chemical modifications. The most abundant modified nucleotide is N6-methyladenosine (m6A), a methyl modification of adenosine. Although early studies viewed m6A as a dynamic and tissue-specific modification, it is now clear that the mRNAs that contain m6A and the location of m6A in those transcripts are largely universal and are influenced by gene architecture, i.e., the size and location of exons and introns. m6A can affect nuclear processes such as splicing and epigenetic regulation, but the major effect of m6A on mRNAs is to promote degradation in the cytoplasm. m6A marks a functionally related cohort of mRNAs linked to certain biological processes, including cell differentiation and cell fate determination. m6A is also enriched in other cohorts of mRNAs and can therefore affect their respective cellular processes and pathways. Future work will focus on understanding how the m6A pathway is regulated to achieve control of m6A-containing mRNAs.
Keywords: METTL14; METTL3; N6-methyladenosine; RBM15; RNA degradation; RNA stability; VIRMA; WTAP; YTHDC1; YTHDC2; YTHDF1; YTHDF2; YTHDF3; ZC3H13; epitranscriptome; m(6)A.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.R.J. is an advisor to, and owns equity in, 858 Therapeutics. S.R.J. is an author of patents related to detection and use of m(6)A in mRNA.
Figures


References
-
- PGENETICS-D-12–00168 [pii].
-
- Bawankar P, Lence T, Paolantoni C, Haussmann IU, Kazlauskiene M, Jacob D, Heidelberger JB, Richter FM, Nallasivan MP, Morin V, et al. (2021). Hakai is required for stabilization of core components of the m6A mRNA methylation machinery. Nat Commun 12, 3778. 10.1038/s41467-021-23892-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

