Childhood encephalitis in the Greater Mekong region (the SouthEast Asia Encephalitis Project): a multicentre prospective study
- PMID: 35714649
- PMCID: PMC9210261
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00174-7
Childhood encephalitis in the Greater Mekong region (the SouthEast Asia Encephalitis Project): a multicentre prospective study
Abstract
Background: Encephalitis is a worldwide public health issue, with a substantially high burden among children in southeast Asia. We aimed to determine the causes of encephalitis in children admitted to hospitals across the Greater Mekong region by implementing a comprehensive state-of-the-art diagnostic procedure harmonised across all centres, and identifying clinical characteristics related to patients' conditions.
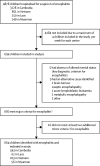
Methods: In this multicentre, observational, prospective study of childhood encephalitis, four referral hospitals in Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar recruited children (aged 28 days to 16 years) who presented with altered mental status lasting more than 24 h and two of the following minor criteria: fever (within the 72 h before or after presentation), one or more generalised or partial seizures (excluding febrile seizures), a new-onset focal neurological deficit, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) white blood cell count of 5 per mL or higher, or brain imaging (CT or MRI) suggestive of lesions of encephalitis. Comprehensive diagnostic procedures were harmonised across all centres, with first-line testing was done on samples taken at inclusion and results delivered within 24 h of inclusion for main treatable causes of disease and second-line testing was done thereafter for mostly non-treatable causes. An independent expert medical panel reviewed the charts and attribution of causes of all the included children. Using multivariate analyses, we assessed risk factors associated with unfavourable outcomes (ie, severe neurological sequelae and death) at discharge using data from baseline and day 2 after inclusion. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04089436, and is now complete.
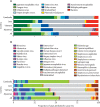
Findings: Between July 28, 2014, and Dec 31, 2017, 664 children with encephalitis were enrolled. Median age was 4·3 years (1·8-8·8), 295 (44%) children were female, and 369 (56%) were male. A confirmed or probable cause of encephalitis was identified in 425 (64%) patients: 216 (33%) of 664 cases were due to Japanese encephalitis virus, 27 (4%) were due to dengue virus, 26 (4%) were due to influenza virus, 24 (4%) were due to herpes simplex virus 1, 18 (3%) were due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, 17 (3%) were due to Streptococcus pneumoniae, 17 (3%) were due to enterovirus A71, 74 (9%) were due to other pathogens, and six (1%) were due to autoimmune encephalitis. Diagnosis was made within 24 h of admission to hospital for 83 (13%) of 664 children. 119 (18%) children had treatable conditions and 276 (42%) had conditions that could have been preventable by vaccination. At time of discharge, 153 (23%) of 664 children had severe neurological sequelae and 83 (13%) had died. In multivariate analyses, risk factors for unfavourable outcome were diagnosis of M tuberculosis infection upon admission (odds ratio 3·23 [95% CI 1·04-10·03]), coma on day 2 (2·90 [1·78-4·72]), supplementary oxygen requirement (1·89 [1·25-2·86]), and more than 1 week duration between symptom onset and admission to hospital (3·03 [1·68-5·48]). At 1 year after inclusion, of 432 children who were discharged alive from hospital with follow-up data, 24 (5%) had died, 129 (30%) had neurological sequelae, and 279 (65%) had completely recovered.
Interpretation: In southeast Asia, most causes of childhood encephalitis are either preventable or treatable, with Japanese encephalitis virus being the most common cause. We provide crucial information that could guide public health policy to improve diagnostic, vaccination, and early therapeutic guidelines on childhood encephalitis in the Greater Mekong region.
Funding: Institut Pasteur, Institut Pasteur International Network, Fondation Merieux, Aviesan Sud, INSERM, Wellcome Trust, Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD), and Fondation Total.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests PB is currently an employee of GSK, this employment has no relation with the study presented here that was initiated at the time he was head of the virology unit at Pasteur Institute in Cambodia. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Childhood encephalitis in the Greater Mekong region: critical to public health policy.Lancet Glob Health. 2022 Jul;10(7):e934-e935. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00208-X. Lancet Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 35714635 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sejvar JJ, Kohl KS, Bilynsky R, et al. Encephalitis, myelitis, and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM): case definitions and guidelines for collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine. 2007;25:5771–5792. - PubMed
-
- Mailles A, De Broucker T, Costanzo P, Martinez-Almoyna L, Vaillant V, Stahl JP. Long-term outcome of patients presenting with acute infectious encephalitis of various causes in France. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:1455–1464. - PubMed
-
- Tyler KL. Acute viral encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:557–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

