Curcumin ameliorated low dose-Bisphenol A induced gastric toxicity in adult albino rats
- PMID: 35715475
- PMCID: PMC9206026
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-14158-1
Curcumin ameliorated low dose-Bisphenol A induced gastric toxicity in adult albino rats
Abstract
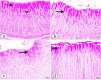
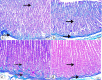
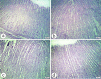
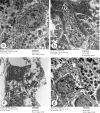
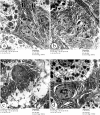
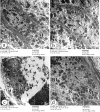
Bisphenol A (BPA) is one of the most common worldwide chemicals involved in the industry of polycarbonate plastics, medical devices, and pharmaceuticals. Forty three-month-old albino rats were randomly classified into four groups. Group Ӏ received a daily corn oil dose (5 mL/kg/ body weight, BW) through a gastric tube for one month, Group ӀӀ received a daily dose of Curcumin (200 mg/kg body weight (B.W.) through a gastric tube for one month, Group ӀӀӀ received a daily dose of BPA (0.5 μg/kg B.W.) through a gastric tube for one month and Group ӀV received concomitant daily doses of Bisphenol A and Curcumin as the regimen described in groups ӀӀ and ӀӀӀ. The rats were sacrificed, and glandular portion of stomach was dissected and processed for light, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. BPA induced destructed gastric glands, dilated congested blood vessels, submucosal oedema, decreased PAS-positive reactivity, increased collagen fibres deposition, decrease in the positive BCL2 immunoexpression, increased positive PCNA immunoexpression, reduction in the gastric mucosal height and destructive changes in the enteroendocrine, chief and parietal cells. Curcumin coadministration provoked an obvious improvement in the gastric structure. BPA exposure has toxic effects on the glandular portion of the stomach in rats. Otherwise, Curcumin coadministration has exhibited protective impact on the architecture of the stomach.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The protective activity of nanomicelle curcumin in bisphenol A-induced cardiotoxicity following subacute exposure in rats.Environ Toxicol. 2019 Mar;34(3):319-329. doi: 10.1002/tox.22687. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Environ Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30496632
-
Antifibrotic effect of curcumin, N-acetyl cysteine and propolis extract against bisphenol A-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: Prophylaxis versus co-treatment.Life Sci. 2020 Nov 1;260:118245. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118245. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32791144
-
Protective potential of curcumin or taurine on nephrotoxicity caused by bisphenol A.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jul;27(19):23994-24003. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08716-1. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32304054
-
Maternal exposure to low-dose bisphenol A and its potential neurotoxic impact on male pups: A histological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study.Tissue Cell. 2024 Oct;90:102503. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2024.102503. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Tissue Cell. 2024. PMID: 39137535
-
Histopathological and biochemical studies on the effect of curcumin and taurine against bisphenol A toxicity in male rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Apr;26(12):12302-12310. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04578-4. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30840252
Cited by
-
Deciphering the molecular mechanism of NLRP3 in BPA-mediated toxicity: Implications for targeted therapies.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 30;10(7):e28917. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28917. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38596095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenols Regulate the Activity of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, Having Both Positive and Negative Effects.J Xenobiot. 2024 Oct 2;14(4):1378-1405. doi: 10.3390/jox14040077. J Xenobiot. 2024. PMID: 39449418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Edible Bird's Nest (EBN) Ameliorates the Effects of Indomethacin (IMC)-Induced Embryo Implantation Dysfunction in Rats.Biology (Basel). 2025 Feb 4;14(2):159. doi: 10.3390/biology14020159. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelzaher W, Ali D, Khalil W. Could Licorice prevent bisphenol a-induced biochemical, histopathological and genetic effects in the adult male Albino rats? Ain Shams J. Forensic Med. Clin. Toxicol. 2018;30(1):73–87. doi: 10.21608/ajfm.2018.18198. - DOI
-
- Yousaf B, Liu G, Wang R, Qadir A, Ali MU, Kanwal Q, Munir B, Abbas Z. Bisphenol A exposure and healing effects of Adiantum capillus-veneris L. plant extract (APE) in bisphenol A-induced reproductive toxicity in albino rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016;23(12):11645–11657. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6330-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

