Cytokine release syndrome-like serum responses after COVID-19 vaccination are frequent and clinically inapparent under cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 35715501
- PMCID: PMC9499865
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-022-00398-7
Cytokine release syndrome-like serum responses after COVID-19 vaccination are frequent and clinically inapparent under cancer immunotherapy
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Cytokine release syndrome-like serum responses after COVID-19 vaccination are frequent and clinically inapparent under cancer immunotherapy.Nat Cancer. 2022 Sep;3(9):1137. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00420-y. Nat Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35840692 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
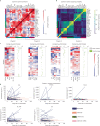
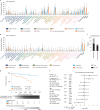
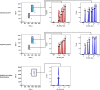
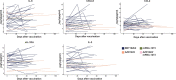
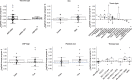
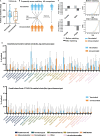
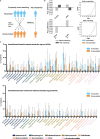
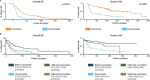
Patients with cancer frequently receive immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), which may modulate immune responses to COVID-19 vaccines. Recently, cytokine release syndrome (CRS) was observed in a patient with cancer who received BTN162b2 vaccination under ICI treatment. Here, we analyzed adverse events and serum cytokines in patients with 23 different tumors undergoing (n = 64) or not undergoing (n = 26) COVID-19 vaccination under ICI therapy in a prospectively planned German single-center cohort study (n = 220). We did not observe clinically relevant CRS (≥grade 2) after vaccination (95% CI 0-5.6%; Common Terminology of Adverse Events v.5.0) in this small cohort. Within 4 weeks after vaccination, serious adverse events occurred in eight patients (12.5% 95% CI 5.6-23%): six patients were hospitalized due to events common under cancer therapy including immune related adverse events and two patients died due to conditions present before vaccination. Despite absence of CRS symptoms, a set of pairwise-correlated CRS-associated cytokines, including CXCL8 and interleukin-6 was >1.5-fold upregulated in 40% (95% CI 23.9-57.9%) of patients after vaccination. Hence, elevated cytokine levels are common and not sufficient to establish CRS diagnosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.W. reports previous and current stock ownership of various pharmaceutical companies manufacturing SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and diagnostics including BionTech, Astra Zeneca and Roche. T.W. also reports research support from CanVirex, a spin-off company of the Heidelberg University Hospital developing viral vector-based immunotherapies and vaccines (financial support for blood sampling materials). G.U. is founder and current CMO/CSO of CanVirex, Basel, Switzerland. G.M.H. reports consulting or advisory roles (unrelated) at Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD Sharp & Dohme, Lilly, Novartis and Daiichi Sankyo; honoraria (unrelated) from Servier, MSD Sharp & Dohme, Lilly, Targos, Bristol-Myers Squibb, IOMEDICO and MCI Conventions; research funding (unrelated) from Nordic Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, MSD Sharp & Dohme, Janssen, Astra Zeneca and IKF Klinische Krebsforschung Frankfurt; and travel/accommodations (unrelated) from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly, Servier and MSD Sharp & Dohme. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Ribas A, et al. Priority COVID-19 Vaccination for Patients with Cancer while Vaccine Supply Is Limited. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:233–236. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1817. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

