Revisiting sea-level budget by considering all potential impact factors for global mean sea-level change estimation
- PMID: 35715517
- PMCID: PMC9205883
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-14173-2
Revisiting sea-level budget by considering all potential impact factors for global mean sea-level change estimation
Abstract
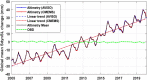
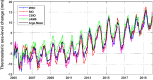
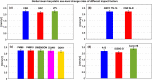
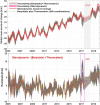
Accurate estimates of global sea-level change from the observations of Altimetry, Argo and Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) and GRACE Follow-on (GRACE-FO) are of great value for investigating the global sea-level budget. In this study, we analyzed the global sea-level change over the period from January 2005 to December 2019 by considering all potential impact factors, i.e. three factors for Altimetry observations (two Altimetry products, ocean bottom deformation (OBD) and glacial isostatic adjustment (GIA)), three factors for Argo observations (four Argo products, salinity product error and deep-ocean steric sea-level change), and seven factors for GRACE/GRACE-FO observations including three official RL06 solutions, five spatial filtering methods, three GIA models, two C20 (degree 2 order 0) products, Geocenter motion, GAD field and global mass conservation. The seven impact factors of GRACE/GRACE-FO observations lead to ninety combinations for the post-procession of global mean barystatic sea-level change estimation, whose rates range from 2.00 to 2.45 mm/year. The total uncertainty of global barystatic sea-level change rate is ± 0.27 mm/year at the 95% confidence level, estimated as the standard deviation of the differences between the different datasets constituting the ensembles. The statistical results show that the preferred GIA model developed by Caron et al. in 2018 can improve the closure of the global sea-level budget by 0.20-0.30 mm/year, which is comparable with that of neglecting the halosteric component. About 30.8% of total combinations (GRACE/GRACE-FO plus Argo) can close the global sea-level budget within 1-sigma (0.23 mm/year) of Altimetry observations, 88.9% within 2-sigma. Once the adopted factors including GRACE/GRACE-FO solutions from Center for Space Research (CSR), Caron18 GIA model, SWENSON filtering and Argo product from China Second Institute of Oceanography, the linear trend of global sterodynamic sea-level change derived from GRACE/GRACE-FO plus Argo observations is 3.85 ± 0.14 mm/year, nearly closed to 3.90 ± 0.23 mm/year of Altimetry observations.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduced misclosure of global sea-level budget with updated Tongji-Grace2018 solution.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 3;11(1):17667. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96880-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34480069 Free PMC article.
-
Uncertainty in GRACE/GRACE-follow on global ocean mass change estimates due to mis-modeled glacial isostatic adjustment and geocenter motion.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 22;12(1):6617. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10628-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35459768 Free PMC article.
-
Barystatic sea level change observed by satellite gravimetry: 1993-2022.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul 8;122(27):e2425248122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2425248122. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40587797 Free PMC article.
-
An Abrupt Decline in Global Terrestrial Water Storage and Its Relationship with Sea Level Change.Surv Geophys. 2024;45(6):1875-1902. doi: 10.1007/s10712-024-09860-w. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Surv Geophys. 2024. PMID: 39734429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Twenty years of ocean observations with China Argo.Hai Yang Xue Bao. 2023;42(2):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s13131-022-2076-3. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Hai Yang Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 36941976 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global and regional ocean mass budget closure since 2003.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 15;15(1):1416. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45726-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38360958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gregory JM, Grifes SM, Hughes CW, et al. Concepts and terminology for sea level: Mean, variability and change, both local and global. Surv. Geophys. 2019;40:1251–1289. doi: 10.1007/s10712-019-09525-z. - DOI
-
- WCRP Global Sea Level Budget Group Global sea level budget 1993-present. Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2018;10:1551–1590. doi: 10.5194/essd-10-1551-2018. - DOI
-
- Chen JL, Tapley B, Save H, Tamisiea ME, Bettadpur S, Ries J. Quantification of ocean mass change using gravity recovery and climate experiment, satellite altimeter, and Argo floats observations. J. Geophys. Res-Sol. Earth. 2018;123:10212–10225. doi: 10.1029/2018JB016095. - DOI
-
- Nerem RS, Chambers DP, Choe C, Mitchum GT. Estimating mean sea level change from the TOPEX and Jason altimeter missions. Mar. Geod. 2010;33(S1):435–446. doi: 10.1080/01490419.2010.491031. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

