A new concept of the fiber composition of cervical spinal dura mater: an investigation utilizing the P45 sheet plastination technique
- PMID: 35715572
- PMCID: PMC9246786
- DOI: 10.1007/s00276-022-02962-3
A new concept of the fiber composition of cervical spinal dura mater: an investigation utilizing the P45 sheet plastination technique
Abstract
Purpose: Few reports have been published regarding the microanatomy of the dura mater located at the craniovertebral junction (CVJ). In clinic, the precise microanatomy of the CVJ dura mater would be taken into account, for reducing surgical complications and ineffective surgical outcomes. The main objective of the present investigation was to further elucidate the fiber composition and sources of the cervical spinal dura mater.
Methods: The formalin-fixed adult head and neck specimens (n = 21) were obtained and P45 plastinated section method was utilized for the present study. The fibers of the upper cervical spinal dura mater (SDM) were examined in the P45 sagittal sections in the CVJ area. All photographic documentation was performed via a Canon EOS 7D Mark camera.
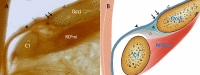
Results: The posterior wall of the SDM sac at CVJ was found to be composed of stratified fibers, which are derived from three sources: the cerebral dura mater, the occipital periosteum, and the myodural bridge (MDB). The proper layer of the cerebral dura mater passes over the brim of the foramen magnum and enters the vertebral canal to form the inner layer of the SDM, and the fibers originating from the periosteum of the brim of the foramen magnum form the middle layer. The fibers of the MDB are inserted into the SDM and form its outer layer. It was found that the total number of fibers from each origin varied in humans.
Conclusion: At the CVJ, the posterior wall of the SDM is a multi-layered structure composed of three different originated fibers. The cerebral dura mater, the periosteum located at the brim of the foramen magnum, and MDB contribute to the formation of the SDM. The present study would be beneficial to the choice of surgical approach at the CVJ and the protection of the SDB.
Keywords: Craniovertebral junction; Microanatomy; P45 plastination; Spinal dura mater.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Orientation and property of fibers of the myodural bridge in humans.Spine J. 2018 Jun;18(6):1081-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29477753
-
Investigation of meningomyovertebral structures within the upper cervical epidural space: a sheet plastination study with clinical implications.Spine J. 2015 Nov 1;15(11):2417-24. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.07.438. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Spine J. 2015. PMID: 26210227
-
Microanatomy of the dura mater at the craniovertebral junction and spinal region for safe and effective surgical treatment.J Neurosurg Spine. 2020 Mar 20;33(2):165-171. doi: 10.3171/2020.1.SPINE191424. Print 2020 Aug 1. J Neurosurg Spine. 2020. PMID: 32197248
-
Connection between the spinal dura mater and suboccipital musculature: evidence for the myodural bridge and a route for its dissection--a review.Clin Anat. 2012 May;25(4):415-22. doi: 10.1002/ca.21261. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Clin Anat. 2012. PMID: 22488993 Review.
-
Utilization of MR imaging in myodural bridge complex with relevant muscles: current status and future perspectives.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020 Sep 1;20(3):382-389. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020. PMID: 32877974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Research status of dural injury types and repair].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Sep 15;37(9):1177-1182. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202306064. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37718434 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A new concept and surgical approach for Chiari malformation type I based on the protection and strengthening of the myodural Bridge.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 19;15(1):9445. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92506-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40108288 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

