Diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence approved for adults for the interpretation of pediatric chest radiographs
- PMID: 35715623
- PMCID: PMC9204675
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-14519-w
Diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence approved for adults for the interpretation of pediatric chest radiographs
Abstract
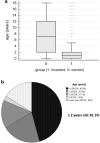
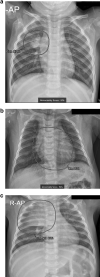
Artificial intelligence (AI) applied to pediatric chest radiographs are yet scarce. This study evaluated whether AI-based software developed for adult chest radiographs can be used for pediatric chest radiographs. Pediatric patients (≤ 18 years old) who underwent chest radiographs from March to May 2021 were included retrospectively. An AI-based lesion detection software assessed the presence of nodules, consolidation, fibrosis, atelectasis, cardiomegaly, pleural effusion, pneumothorax, and pneumoperitoneum. Using the pediatric radiologist's results as standard reference, we assessed the diagnostic performance of the software. For the total 2273 chest radiographs, the AI-based software showed a sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of 67.2%, 91.1%, 57.7%, 93.9%, and 87.5%, respectively. Age was a significant factor for incorrect results (odds radio 0.821, 95% confidence interval 0.791-0.851). When we excluded cardiomegaly and children 2 years old or younger, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy significantly increased (86.4%, 97.9%, 79.7%, 98.7% and 96.9%, respectively, all p < 0.001). In conclusion, AI-based software developed with adult chest radiographs showed diagnostic accuracies up to 96.9% for pediatric chest radiographs when we excluded cardiomegaly and children 2 years old or younger. AI-based lesion detection software needs to be validated in younger children.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimizing adult-oriented artificial intelligence for pediatric chest radiographs by adjusting operating points.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82775-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732934 Free PMC article.
-
Commercially Available Chest Radiograph AI Tools for Detecting Airspace Disease, Pneumothorax, and Pleural Effusion.Radiology. 2023 Sep;308(3):e231236. doi: 10.1148/radiol.231236. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 37750768
-
Using AI to Improve Radiologist Performance in Detection of Abnormalities on Chest Radiographs.Radiology. 2023 Dec;309(3):e230860. doi: 10.1148/radiol.230860. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 38085079
-
Current and emerging artificial intelligence applications in chest imaging: a pediatric perspective.Pediatr Radiol. 2022 Oct;52(11):2120-2130. doi: 10.1007/s00247-021-05146-0. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Pediatr Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34471961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitivity of bedside ultrasound and supine anteroposterior chest radiographs for the identification of pneumothorax after blunt trauma.Acad Emerg Med. 2010 Jan;17(1):11-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2009.00628.x. Acad Emerg Med. 2010. PMID: 20078434 Review.
Cited by
-
Three-Stage Framework for Accurate Pediatric Chest X-ray Diagnosis Using Self-Supervision and Transfer Learning on Small Datasets.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 29;14(15):1634. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14151634. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125510 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Based Software with CE Mark for Chest X-ray Interpretation: Opportunities and Challenges.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 10;13(12):2020. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13122020. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethical considerations in AI for child health and recommendations for child-centered medical AI.NPJ Digit Med. 2025 Mar 10;8(1):152. doi: 10.1038/s41746-025-01541-1. NPJ Digit Med. 2025. PMID: 40065130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidentally found resectable lung cancer with the usage of artificial intelligence on chest radiographs.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 10;18(3):e0281690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281690. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36897865 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for pediatric chest x-ray diagnosis: Repurposing a commercial tool developed for adults.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 24;20(7):e0328295. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328295. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40705715 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

