Prevalence, Outcome, and Prevention of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection in Neonates Born to Women With Preconception Immunity (CHILd Study)
- PMID: 35717635
- PMCID: PMC9907511
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciac482
Prevalence, Outcome, and Prevention of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection in Neonates Born to Women With Preconception Immunity (CHILd Study)
Abstract
Background: Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is the leading infectious cause of congenital disabilities. We designed a prospective study to investigate the rate, outcome, and risk factors of congenital CMV (cCMV) infection in neonates born to immune women, and the potential need and effectiveness of hygiene recommendations in this population.
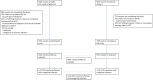
Methods: The study was composed of 2 sequential parts: an epidemiology (part 1) and a prevention (part 2) study. Performance of part 2 depended upon a cCMV rate >0.4%. Women enrolled in part 1 did not receive hygiene recommendations. Newborns were screened by HCMV DNA testing in saliva and cCMV was confirmed by urine testing.
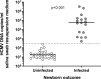
Results: Saliva swabs were positive for HCMV DNA in 45/9661 newborns and cCMV was confirmed in 18 cases. The rate of cCMV was .19% (95% confidence interval [CI]: .11-.29%), and 3 out of 18 infants with cCMV had symptoms of CMV at birth. Age, nationality, occupation, and contact with children were similar between mothers of infected and noninfected newborns. Twin pregnancy (odds ratio [OR]: 7.2; 95% CI: 1.7-32.2; P = .037) and maternal medical conditions (OR: 3.9; 95% CI: 1.5-10.1; P = .003) appeared associated with cCMV. Given the rate of cCMV was lower than expected, the prevention part of the study was cancelled.
Conclusions: Newborns from women with preconception immunity have a low rate of cCMV, which appears to be mostly due to reactivation of the latent virus. Therefore, serological screening in childbearing age would be pivotal to identify HCMV-seropositive women, whose newborns have a low risk of cCMV.
Clinical trials registration: www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03973359).
Keywords: congenital infection; human cytomegalovirus; nonprimary infection; preconception immunity.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. The authors: No reported conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Kenneson A, Cannon MJ. Review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Rev Med Virol 2007; 17:253–76. - PubMed
-
- Stagno S, Pass RF, Cloud G, et al. . Primary cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy. Incidence, transmission to the fetus and clinical outcome. JAMA 1986; 256:1904–8. - PubMed
-
- Dollard SC, Grosse SD, Ross DS. New estimates of the prevalence of neurological and sensory sequelae and mortality associated with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Rev Med Virol 2007; 17:355–63. - PubMed

