Development of Biodegradable Osteopromotive Citrate-Based Bone Putty
- PMID: 35717669
- PMCID: PMC9463100
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.202203003
Development of Biodegradable Osteopromotive Citrate-Based Bone Putty
Abstract
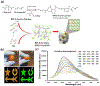
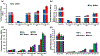
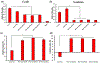
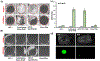
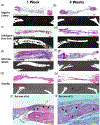
The burden of bone fractures demands development of effective biomaterial solutions, while additional acute events such as noncompressible bleeding further motivate the search for multi-functional implants to avoid complications including osseous hemorrhage, infection, and nonunion. Bone wax has been widely used in orthopedic bleeding control due to its simplicity of use and conformation to irregular defects; however, its nondegradability results in impaired bone healing, risk of infection, and significant inflammatory responses. Herein, a class of intrinsically fluorescent, osteopromotive citrate-based polymer/hydroxyapatite (HA) composites (BPLP-Ser/HA) as a highly malleable press-fit putty is designed. BPLP-Ser/HA putty displays mechanics replicating early nonmineralized bone (initial moduli from ≈2-500 kPa), hydration induced mechanical strengthening in physiological conditions, tunable degradation rates (over 2 months), low swelling ratios (<10%), clotting and hemostatic sealing potential (resistant to blood pressure for >24 h) and significant adhesion to bone (≈350-550 kPa). Simultaneously, citrate's bioactive properties result in antimicrobial (≈100% and 55% inhibition of S. aureus and E. coli) and osteopromotive effects. Finally, BPLP-Ser/HA putty demonstrates in vivo regeneration in a critical-sized rat calvaria model equivalent to gold standard autograft. BPLP-Ser/HA putty represents a simple, off-the-shelf solution to the combined challenges of acute wound management and subsequent bone regeneration.
Keywords: bone putty; bone wax; citric acid; metabonegenesis; orthopedic biomaterials.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
Dr. Jian Yang and The Pennsylvania State University have a financial interest in Acuitive Technologies, Inc. and Aleo BME, Inc. These interests have been reviewed by the University’s Institutional and Individual Conflict of Interest Committees and are currently being managed by the University.
Figures



References
-
- Massimo M, Timothy RA, Bone Res. 2013, 1 (3), 203–215.
-
- Allen-Wilson N, Beatty R, Sharpe J, J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2015, 105 (1), 74–79. - PubMed
-
- Claudio S, Enrico T, Giuseppe B, Vincenzo A, Aldo M, Eur Spine J. 2004, 13, S89–S96.
-
- Laurel G, Anthony K, Philip W, John EC Jr., Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2004, 25 (4), 346–348.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

