Recognition of Gallotannins and the Physiological Activities: From Chemical View
- PMID: 35719149
- PMCID: PMC9198600
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.888892
Recognition of Gallotannins and the Physiological Activities: From Chemical View
Abstract
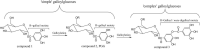
Gallotannins, characterized with the glycosidic core and galloyl unit, are seemed as vital components of hydrolyzable tannins. Benefit from the more and more discoveries of their bioactivities and edibility, application of gallotannins in food industry, pharmacy industry, and other fields is increasing. Inheriting previous study achievements, chemical structure of gallotannins was illustrated and degradation as well as synthetic routes to gallotannins were summarized. On this basis, distribution in the nature also including the distinction of gallotannins was discussed. More than that, activities involving in antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, enzyme inhibitions, protein binding, and so on, as well as applications in the field of food industry, biopharmaceutical science, agricultural production, etc., were combed. Finally, improvement of bioavailability, chemical modification of the structure, and accurate determination of new gallotannins were pointed out to be the orientation in the future.
Keywords: gallotannins; industrial application; physiological activities; resource distribution; structural characteristic.
Copyright © 2022 He.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Seguin A. Ann. Chim (Paris, Fr.). (1976) 20:15.
-
- Watson RR. Nutrition and Functional Foods for Healthy Aging, Chapter 18-Polyphenols and Intestinal Health. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; (2017). p. 191–210.
-
- Tollefsbol TO. Medical Epigenetics, Chapter 39-Natural Epigenetic-Modifying Molecules in Medical Therapy. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; (2016). p. 747–98.
-
- Haslam E, Haworth RD, Jones K, Rogers HJ. Gallotannins. Part I. Introduction and the Fractionation of Tannase. J Chem Soc. (1961) 1829–35. 10.1039/jr9610001829 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources