Representation Learning: Recommendation With Knowledge Graph via Triple-Autoencoder
- PMID: 35719384
- PMCID: PMC9204654
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.891265
Representation Learning: Recommendation With Knowledge Graph via Triple-Autoencoder
Abstract
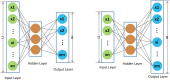
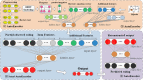
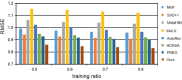
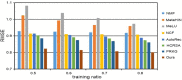
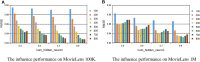
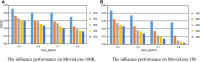
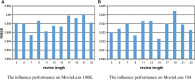
The last decades have witnessed a vast amount of interest and research in feature representation learning from multiple disciplines, such as biology and bioinformatics. Among all the real-world application scenarios, feature extraction from knowledge graph (KG) for personalized recommendation has achieved substantial performance for addressing the problem of information overload. However, the rating matrix of recommendations is usually sparse, which may result in significant performance degradation. The crucial problem is how to extract and extend features from additional side information. To address these issues, we propose a novel feature representation learning method for the recommendation in this paper that extends item features with knowledge graph via triple-autoencoder. More specifically, the comment information between users and items is first encoded as sentiment classification. These features are then applied as the input to the autoencoder for generating the auxiliary information of items. Second, the item-based rating, the side information, and the generated comment representations are incorporated into the semi-autoencoder for reconstructed output. The low-dimensional representations of this extended information are learned with the semi-autoencoder. Finally, the reconstructed output generated by the semi-autoencoder is input into a third autoencoder. A serial connection between the semi-autoencoder and the autoencoder is designed here to learn more abstract and higher-level feature representations for personalized recommendation. Extensive experiments conducted on several real-world datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed method compared to several state-of-the-art models.
Keywords: autoencoder; collaborative filtering; personalized recommendation; representation learning; semi-autoencoder.
Copyright © 2022 Geng, Xiao, Sun and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor YD declared a past co-authorship with the author XS.
Figures
References
-
- Batmaz Z., Yurekli A., Bilge A., Kaleli C. (2019). A Review on Deep Learning for Recommender Systems: Challenges and Remedies. Artif. Intell. Rev. 52 (1), 1–37. 10.1007/s10462-018-9654-y - DOI
-
- Bengio Y. (2009). Learning Deep Architectures for AI. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 2 (1), 1–127. 10.1561/2200000006 - DOI
-
- Botangen K. A., Yu J., Sheng Q. Z., Han Y., Yongchareon S. (2020). Geographic-Aware Collaborative Filtering for Web Service Recommendation. Expert Syst. Appl. 151, 113347. 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113347 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

