The Co-infection of Mild COVID-19 and Rhinocerebral Mucormycosis in a Patient Without Diabetes or Prior Steroid Use
- PMID: 35719782
- PMCID: PMC9189617
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.24986
The Co-infection of Mild COVID-19 and Rhinocerebral Mucormycosis in a Patient Without Diabetes or Prior Steroid Use
Abstract
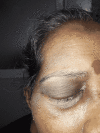
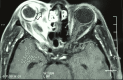
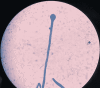
In a fast-evolving COVID-19 pandemic, co-infection with mucormycosis has been reported in some parts of the world. It is still unknown whether one of the either diseases makes the patient susceptible to developing the other. The co-occurrence of them significantly elevates the mortality risk and is commonly reported in immunocompromised individuals. We herein report a case of COVID-19 infection with rhinocerebral mucormycosis without prior steroid use or underlying immunosuppressive diseases.
Keywords: antifungal drugs; covid 19; diabetes type 2; rhinocerebral mucormycosis; steroid use.
Copyright © 2022, Sekar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Rhinocerebral mucormycosis. Pillsbury HC, Fischer ND. Arch Otolaryngol. 1977;103:600–604. - PubMed
-
- Hospitalized Adults: Therapeutic Management. [ May; 2022 ];https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinical-manag... 2022
-
- Mucormycosis (Zygomycosis): Background, Etiology and Pathophysiology, Epidemiology. [ May; 2022 ];https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/222551-overview 2022
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
