Wing-feather loss in white-feathered laying hens decreases pectoralis thickness but does not increase risk of keel bone fracture
- PMID: 35719889
- PMCID: PMC9198519
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.220155
Wing-feather loss in white-feathered laying hens decreases pectoralis thickness but does not increase risk of keel bone fracture
Abstract
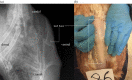
Feather loss in domestic chickens can occur due to wear and tear, disease or bird-to-bird pecking. Flight feather loss may decrease wing use, cause pectoral muscle loss and adversely impact the keel bone to which these muscles anchor. Feather loss and muscle weakness are hypothesized risk factors for keel bone fractures that are reported in up to 98% of chickens. We used ultrasound to measure changes in pectoral muscle thickness and X-rays to assess keel bone fracture prevalence following symmetric clipping of primary and secondary feathers in white- and brown-feathered birds. Four and six weeks after flight feather clipping, pectoralis thickness decreased by approximately 5%, while lower leg thickness increased by approximately 5% in white-feathered birds. This pectoralis thickness decrease may reflect wing disuse followed by muscle atrophy, while the increased leg thickness may reflect increased bipedal locomotion. The lack of effect on muscle thickness in brown-feathered hens was probably due to their decreased tendency for aerial locomotion. Finally, pectoralis thickness was not associated with keel bone fractures in either white- or brown-feathered birds. This suggests that the white-feathered strain was more sensitive to feather loss. Future prevention strategies should focus on birds most susceptible to muscle loss associated with flight feather damage.
Keywords: bird; feather loss; flapping flight; keel bone damage; muscle adaptations.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Edwards CL. 1886. The relation of the pectoral muscles of birds to the power of flight. Am. Nat. 20, 25-29. (10.1086/274137) - DOI
-
- Piersma T, Gill RE, Ruthrauff DR. 2021. Physiomorphic transformation in extreme endurance migrants: revisiting the case of bar-tailed godwits preparing for trans-Pacific flights. Front. Ecol. Evol. 9, 1-8. (10.3389/fevo.2021.685764) - DOI
-
- Landys-Ciannelli MM, Piersma T, Jukema J. 2003. Strategic size changes of internal organs and muscle tissue in the bar-tailed godwit during fat storage on a spring stopover site. Funct. Ecol. 17, 151-159. (10.1046/j.1365-2435.2003.00715.x) - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
