Predicting Lapatinib Dose Regimen Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques Based on a Real-World Study
- PMID: 35719963
- PMCID: PMC9203846
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.893966
Predicting Lapatinib Dose Regimen Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques Based on a Real-World Study
Abstract
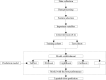
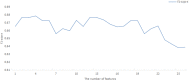
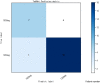
Lapatinib is used for the treatment of metastatic HER2(+) breast cancer. We aim to establish a prediction model for lapatinib dose using machine learning and deep learning techniques based on a real-world study. There were 149 breast cancer patients enrolled from July 2016 to June 2017 at Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. The sequential forward selection algorithm based on random forest was applied for variable selection. Twelve machine learning and deep learning algorithms were compared in terms of their predictive abilities (logistic regression, SVM, random forest, Adaboost, XGBoost, GBDT, LightGBM, CatBoost, TabNet, ANN, Super TML, and Wide&Deep). As a result, TabNet was chosen to construct the prediction model with the best performance (accuracy = 0.82 and AUC = 0.83). Afterward, four variables that strongly correlated with lapatinib dose were ranked via importance score as follows: treatment protocols, weight, number of chemotherapy treatments, and number of metastases. Finally, the confusion matrix was used to validate the model for a dose regimen of 1,250 mg lapatinib (precision = 81% and recall = 95%), and for a dose regimen of 1,000 mg lapatinib (precision = 87% and recall = 64%). To conclude, we established a deep learning model to predict lapatinib dose based on important influencing variables selected from real-world evidence, to achieve an optimal individualized dose regimen with good predictive performance.
Keywords: TabNet; breast cancer; deep learning; individualized medication model; lapatinib; machine learning; real-world study.
Copyright © 2022 Yu, Ye, Liu, Li, Hao, Zhang, Kou, Wang, Wei, Gao and Zhai.
Conflict of interest statement
Author JZ and FG are employed by Beijing Medicinovo Technology Co. Ltd., China. Author XH is employed by Dalian Medicinovo Technology Co., Ltd., China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An individualized medication model of sodium valproate for patients with bipolar disorder based on machine learning and deep learning techniques.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 17;13:890221. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.890221. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339624 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based prediction of sertraline concentration in patients with depression through therapeutic drug monitoring.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 6;15:1289673. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1289673. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38510645 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-based model for dose prediction of sertraline in adolescents: a real-world study.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Jun;17(2):177-187. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2024.2304009. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38197873
-
Personalized venlafaxine dose prediction using artificial intelligence technology: a retrospective analysis based on real-world data.Int J Clin Pharm. 2024 Aug;46(4):926-936. doi: 10.1007/s11096-024-01729-7. Epub 2024 May 11. Int J Clin Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38733475
-
Construction and evaluation of glucocorticoid dose prediction model based on genetic and clinical characteristics of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2025 Jan-Dec;39:3946320251331791. doi: 10.1177/03946320251331791. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40186486 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dose-sparing effect of lapatinib co-administered with a high-fat enteral nutrition emulsion: preclinical pharmacokinetic study.PeerJ. 2023 Oct 9;11:e16207. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16207. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37842056 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Methods for Precision Dosing in Anticancer Drug Therapy: A Scoping Review.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2024 Sep;63(9):1221-1237. doi: 10.1007/s40262-024-01409-9. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2024. PMID: 39153056 Free PMC article.
-
A model for identifying potentially inappropriate medication used in older people with dementia: a machine learning study.Int J Clin Pharm. 2024 Aug;46(4):937-946. doi: 10.1007/s11096-024-01730-0. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Int J Clin Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38980590 Free PMC article.
-
Bimodal artificial intelligence using TabNet for differentiating spinal cord tumors-Integration of patient background information and images.iScience. 2023 Sep 14;26(10):107900. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107900. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37766987 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning in onco-pharmacogenomics: a path to precision medicine with many challenges.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 9;14:1260276. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1260276. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38264526 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous