CD3D Is an Independent Prognostic Factor and Correlates With Immune Infiltration in Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 35719985
- PMCID: PMC9198637
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.913670
CD3D Is an Independent Prognostic Factor and Correlates With Immune Infiltration in Gastric Cancer
Abstract
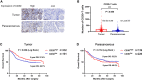
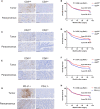
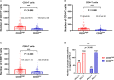
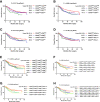
The protein encoded by CD3D is part of the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex (TCR/CD3 complex) and is involved in T-cell development and signal transduction. Previous studies have shown that CD3D is associated with prognosis and treatment response in breast, colorectal, and liver cancer. However, the expression and clinical significance of CD3D in gastric cancer are not clear. In this study, we collected 488 gastric cancer tissues and 430 paired adjacent tissues to perform tissue microarrays (TMAs). Then, immunohistochemical staining of CD3D, CD3, CD4, CD8 and PD-L1 was conducted to investigate the expression of CD3D in gastric cancer and the correlation between the expression of CD3D and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and PD-L1. The results showed that CD3D was highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues compared with paracancerous tissues (P<0.000). Univariate and multivariate analyses showed that CD3D was an independent good prognostic factor for gastric cancer (P=0.004, HR=0.677, 95%CI: 0.510-0.898 for univariate analyses; P=0.046, HR=0.687, 95%CI: 0.474-0.994 for multivariate analyses). In addition, CD3D was negatively correlated with the tumor location, Borrmann type and distant metastasis (P=0.012 for tumor location; P=0.007 for Borrmann type; P=0.027 for distant metastasis). In addition, the expression of CD3D was highly positively correlated with the expression of CD3, CD4, CD8, and PD-L1, and the combination of CD3D with CD3, CD4, CD8 and PD-L1 predicted the best prognosis (P=0.043). In summary, CD3D may play an important regulatory role in the tumor immune microenvironment of gastric cancer and may serve as a potential indicator of prognosis and immunotherapy response.
Keywords: PD-L1; cd3d; gastric cancer; prognosis; tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs).
Copyright © 2022 Yuan, Xu, Shi, Jin, Bao, Yu, Wang, Xia, Qin, Zhang and Yao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High CD3D/CD4 ratio predicts better survival in muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Apr 12;11:2987-2995. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S191105. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31114346 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Prognostic Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and PD-L1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Feb 25;14:1377-1385. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S289720. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33658801 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive relevance of PD-L1 expression with pre-existing TILs in gastric cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 26;8(59):99372-99381. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22079. eCollection 2017 Nov 21. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29245908 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Intra-Tumoral Immune Response and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Gastric Cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Sep 14;25:6916-6921. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916432. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31519868 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Jun;132:71-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.03.013. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32334338
Cited by
-
Single-Cell Sequencing Combined with Transcriptome Sequencing Constructs a Predictive Model of Key Genes in Multiple Sclerosis and Explores Molecular Mechanisms Related to Cellular Communication.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jan 9;17:191-210. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S442684. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38226354 Free PMC article.
-
ERCC1 is a potential biomarker for predicting prognosis, immunotherapy, chemotherapy efficacy, and expression validation in HER2 over-expressing breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 20;12:955719. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.955719. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36338712 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of the novel immune risk scoring system related to CD8+ T cells in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Jun 22;23(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02966-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37349706 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Subtypes and Characteristics of Endometrial Cancer Based on Immunogenes.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Oct 29;16:1525-1543. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S494838. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39493321 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic biomarker CD3G that correlates with the tumor microenvironment in cervical cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 13;12:979226. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.979226. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36176400 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

