Investigating the Anticancer Potential of Salvicine as a Modulator of Topoisomerase II and ROS Signaling Cascade
- PMID: 35719997
- PMCID: PMC9198638
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.899009
Investigating the Anticancer Potential of Salvicine as a Modulator of Topoisomerase II and ROS Signaling Cascade
Abstract
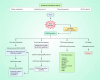
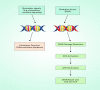
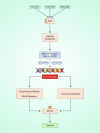
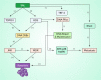
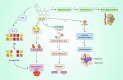
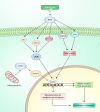
Salvicine is a new diterpenoid quinone substance from a natural source, specifically in a Chinese herb. It has powerful growth-controlling abilities against a broad range of human cancer cells in both in vitro and in vivo environments. A significant inhibitory effect of salvicine on multidrug-resistant (MDR) cells has also been discovered. Several research studies have examined the activities of salvicine on topoisomerase II (Topo II) by inducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) signaling. As opposed to the well-known Topo II toxin etoposide, salvicine mostly decreases the catalytic activity with a negligible DNA breakage effect, as revealed by several enzymatic experiments. Interestingly, salvicine dramatically reduces lung metastatic formation in the MDA-MB-435 orthotopic lung cancer cell line. Recent investigations have established that salvicine is a new non-intercalative Topo II toxin by interacting with the ATPase domains, increasing DNA-Topo II interaction, and suppressing DNA relegation and ATP hydrolysis. In addition, investigations have revealed that salvicine-induced ROS play a critical role in the anticancer-mediated signaling pathway, involving Topo II suppression, DNA damage, overcoming multidrug resistance, and tumor cell adhesion suppression, among other things. In the current study, we demonstrate the role of salvicine in regulating the ROS signaling pathway and the DNA damage response (DDR) in suppressing the progression of cancer cells. We depict the mechanism of action of salvicine in suppressing the DNA-Topo II complex through ROS induction along with a brief discussion of the anticancer perspective of salvicine.
Keywords: DNA damage response (DDR); ROS signaling; anticancer properties; diterpenoid quinone; multidrug-resistant (MDR); topoisomerase II.
Copyright © 2022 Dey, Hasan, Biswas, Papadakos, Rayan, Tasnim, Bilal, Islam, Arshe, Arshad, Farzana, Rahaman, Baral, Paul, Bibi, Rahman and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salvicine, a novel topoisomerase II inhibitor, exerts its potent anticancer activity by ROS generation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007 Sep;28(9):1460-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00698.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007. PMID: 17723179 Review.
-
Salvicine, a novel DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor, exerting its effects by trapping enzyme-DNA cleavage complexes.Biochem Pharmacol. 2001 Sep 15;62(6):733-41. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(01)00732-8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11551518
-
Reactive oxygen species elicit apoptosis by concurrently disrupting topoisomerase II and DNA-dependent protein kinase.Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Oct;68(4):983-94. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.011544. Epub 2005 Jul 15. Mol Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16024664
-
Salvicine functions as novel topoisomerase II poison by binding to ATP pocket.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;70(5):1593-601. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.027714. Epub 2006 Aug 16. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16914642
-
Antitumor triptycene bisquinones: a novel synthetic class of dual inhibitors of DNA topoisomerase I and II activities.Anticancer Drugs. 2003 Aug;14(7):503-14. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200308000-00002. Anticancer Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12960734 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-adherent effects of Rhizophora apiculata bark and leaf extracts and computational prediction of the effects of its compound on β-tubulin interaction in Acanthamoeba triangularis genotype 4.Vet World. 2024 Dec;17(12):2829-2845. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.2829-2845. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 39897349 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the potent TOPO IIα inhibitors in breast cancer through the study of computational drug discovery research approaches.Mol Divers. 2025 Feb;29(1):655-670. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10882-0. Epub 2024 May 21. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 38773015
-
Phyllanthus emblica (Amla) methanolic extract regulates multiple checkpoints in 15-lipoxygenase mediated inflammopathies: Computational simulation and in vitro evidence.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Aug;31(8):101681. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.06.014. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37576860 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating gastric cancer mechanisms and therapeutic potential of Adociaquinone A targeting EGFR: A genomic analysis and Computer Aided Drug Design (CADD) approach.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Oct;28(20):e70133. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70133. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39434198 Free PMC article.
-
Study of MDM2 as Prognostic Biomarker in Brain-LGG Cancer and Bioactive Phytochemicals Inhibit the p53-MDM2 Pathway: A Computational Drug Development Approach.Molecules. 2023 Mar 27;28(7):2977. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072977. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morounke SG, Ayorinde JB, Benedict AO, Adedayo FF, et al. . Epidemiology and Incidence of Common Cancers in Nigeria. J Cancer Biol Res (2017) 5(3):1105.
-
- Al Saber M, Biswas P, Dey D, Kaium M, Islam M, Tripty MIA, et al. . Comprehensive Review of Recent Advancements in Cancer Immunotherapy and Generation of CAR T Cell by CRISPR-Cas9. Processes (2022) 10:16. doi: 10.3390/pr10010016 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

