Change of Serum Biomarkers to Post-Thrombolytic Symptomatic Intracranial Hemorrhage in Stroke
- PMID: 35720096
- PMCID: PMC9202348
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.889746
Change of Serum Biomarkers to Post-Thrombolytic Symptomatic Intracranial Hemorrhage in Stroke
Abstract
Background: Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) is a terrible complication after intravenous alteplase in stroke, and numerous biomarkers have been investigated. However, the change of biomarkers to sICH has not been well determined.
Aim: To investigate the association between the change of biomarkers and sICH.
Methods: This is a prospective cohort study, and patients with sICH within 24 h after thrombolysis were enrolled, while patients without sICH were matched by propensity score matching with a ratio of 1:1. The blood samples were collected before and 24 h after intravenous thrombolysis (IVT), and preset 49 serum biomarkers were measured by microarray analysis. Protein function enrichment analyses were performed to detect the association between the change of biomarkers and sICH.
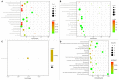
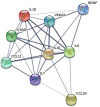
Results: Of consecutive 358 patients, 7 patients with sICH in 24 h were assigned to the sICH group, while 7 matched patients without any ICH were assigned to the non-sICH group. A total of 9 biomarkers were found to significantly change before vs. after thrombolysis between groups, including increased biomarkers, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor, C-C motif chemokine ligand (CCL)-24, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, IL-18, and vascular endothelial growth factor, and decreased biomarkers, such as CCL-11, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and IL-7.
Conclusions: This is the first study to identify changes in serum biomarkers in patients with sICH after IVT, and found that 6 neuroinflammatory and 3 neuroprotective biomarkers may be associated with brain injury following post-thrombolytic sICH.
Clinical trial registration: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov, identifier: NCT02854592.
Keywords: alteplase; biomarkers; intravenous thrombolysis; microarray analysis; symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage.
Copyright © 2022 Cui, Wang, Zhao, Chen, Sheng, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Larrue V, von Kummer R R, Müller A, Bluhmki E. Risk factors for severe hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: a secondary analysis of the European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study (ECASS II). Stroke. (2001) 32:438–41. 10.1161/01.STR.32.2.438 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

