RAB42 is a Potential Biomarker that Correlates With Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35720121
- PMCID: PMC9204584
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.898567
RAB42 is a Potential Biomarker that Correlates With Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
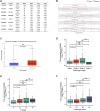
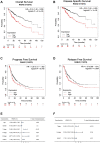
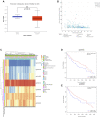
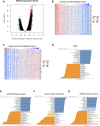
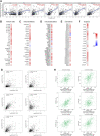
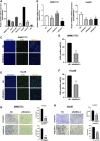
Backgrounds: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant cancer with high mortality. Previous studies have reported that RAB42 is associated with prognosis and progression in glioma. However, the role of RAB42 in HCC is still unknown. Therefore, we aimed to elucidate the value of RAB42 in the predicting prognosis of HCC, and its relationship with immune cells infiltration. Methods: UALCAN, HCCDB, and MethSurv databases were used to examine the expression and methylation levels of RAB42 in HCC and normal samples. cBioPortal and MethSurv were used to identify genetic alterations and DNA methylation of RAB42, and their effect on prognosis. The correlations between RAB42 and the immune cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts infiltration were analyzed by TIMER, TISIDB, and GEPIA database. The LinkedOmics database was used to analyze the enriched pathways associated with genes co-expressed with RAB42. EdU assay was used to evaluate the proliferation ability of liver cancer cells, and transwell assay was used to detect the invasion and migration ability of liver cancer cells. Results: The expression levels of RAB42 were increased in HCC tissues than that in normal tissues. Highly expressed RAB42 was significantly correlated with several clinical parameters of HCC patients. Moreover, increased RAB42 expression clearly predicted poor prognosis in HCC. Furthermore, multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that RAB42 was an independent prognostic factor in HCC. The RAB42 genetic alteration rate was 5%. RAB42 DNA methylation in HCC tissues was lower than that in normal tissues. Among the 7 DNA methylation CpG sites, two were related to the prognosis of HCC. The results of gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) showed that RAB42 was associated with various immune cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts infiltration in HCC. Meanwhile, we found RAB42 methylation was strongly correlated with immune infiltration levels, immunomodulators, and chemokines. Experiments in vitro indicated that knockdown of RAB42 inhibited the proliferation, invasion, and migration of liver cancer cells. Conclusions: Our study highlights the clinical importance of RAB42 in HCC and explores the effect of RAB42 on immune infiltration in the tumor microenvironment, and RAB42 may act as a pro-oncogene that promotes HCC progression.
Keywords: CAFs; HCC; RAB42; biomarker; immune infiltration.
Copyright © 2022 Peng, Du and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
RAB42 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis, immune cell infiltration and chemoresistance.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1445170. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1445170. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39101146 Free PMC article.
-
RAB6B is a potential prognostic marker and correlated with the remolding of tumor immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 2;13:989655. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.989655. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120364 Free PMC article.
-
CPNE1 is a potential prognostic biomarker, associated with immune infiltrates and promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Feb 9;22(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02485-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35139863 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of PDZ-binding kinase is correlated with poor prognosis and immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Jan 22;20(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02479-w. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35065633 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic summarization of the expression profiles and prognostic roles of the dishevelled gene family in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Sep;8(9):e1384. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1384. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32588988 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of APOC1 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression and Serves as a Potential Therapeutic Target Based on Bioinformatics Analysis.J Oncol. 2023 Mar 1;2023:2611105. doi: 10.1155/2023/2611105. eCollection 2023. J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36908705 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Role of Epigenetic Methylation Modification in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jun 17;11:1143-1156. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S458734. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38911291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pan-Cancer Analysis of the Roles and Driving Forces of RAB42.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 26;13(1):43. doi: 10.3390/biom13010043. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36671428 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NTRK Fusion Genes in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment of HPV (+/-) Cervical Cancer.J Med Virol. 2025 Aug;97(8):e70564. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70564. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 40832845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAB42 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis, immune cell infiltration and chemoresistance.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1445170. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1445170. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39101146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beltra J.-C., Manne S., Abdel-Hakeem M. S., Kurachi M., Giles J. R., Chen Z., et al. (2020). Developmental Relationships of Four Exhausted CD8+ T Cell Subsets Reveals Underlying Transcriptional and Epigenetic Landscape Control Mechanisms. Immunity 52, 825–841. 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

