Chemical Communication in Artificial Cells: Basic Concepts, Design and Challenges
- PMID: 35720123
- PMCID: PMC9199989
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.880525
Chemical Communication in Artificial Cells: Basic Concepts, Design and Challenges
Abstract
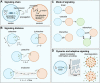
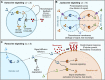
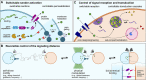
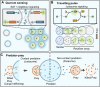
In the past decade, the focus of bottom-up synthetic biology has shifted from the design of complex artificial cell architectures to the design of interactions between artificial cells mediated by physical and chemical cues. Engineering communication between artificial cells is crucial for the realization of coordinated dynamic behaviours in artificial cell populations, which would have implications for biotechnology, advanced colloidal materials and regenerative medicine. In this review, we focus our discussion on molecular communication between artificial cells. We cover basic concepts such as the importance of compartmentalization, the metabolic machinery driving signaling across cell boundaries and the different modes of communication used. The various studies in artificial cell signaling have been classified based on the distance between sender and receiver cells, just like in biology into autocrine, juxtacrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling. Emerging tools available for the design of dynamic and adaptive signaling are highlighted and some recent advances of signaling-enabled collective behaviours, such as quorum sensing, travelling pulses and predator-prey behaviour, are also discussed.
Keywords: artificial cells; bottom-up synthetic biology; chemical signaling; collective behaviours; dynamic colloidal systems; systems chemistry.
Copyright © 2022 Karoui, Patwal, Pavan Kumar and Martin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bottom-Up Synthesis of Artificial Cells: Recent Highlights and Future Challenges.Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2021 Jun 7;12:287-308. doi: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-092220-085918. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2021. PMID: 34097845
-
Light-Activated Signaling in DNA-Encoded Sender-Receiver Architectures.ACS Nano. 2020 Nov 24;14(11):15992-16002. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c07537. Epub 2020 Oct 20. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 33078948 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Cells: Synthetic Compartments with Life-like Functionality and Adaptivity.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Apr 18;50(4):769-777. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00512. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28094501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinspired Networks of Communicating Synthetic Protocells.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Dec 24;8:804717. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.804717. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 35004855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering cell-cell signaling.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013 Oct;24(5):940-947. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23856592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal Communication in Artificial Cell Consortia for Dynamic Control of DNA Nanostructures.ACS Cent Sci. 2024 Jul 22;10(8):1619-1628. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00702. eCollection 2024 Aug 28. ACS Cent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39220708 Free PMC article.
-
Models of Chemical Communication for Micro/Nanoparticles.Acc Chem Res. 2024 Mar 19;57(6):815-830. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00619. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38427324 Free PMC article.
-
Light-Based Juxtacrine Signaling Between Synthetic Cells.Small Sci. 2024 Oct 30;5(1):2400401. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400401. eCollection 2025 Jan. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40212648 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial molecular communication network based on DNA nanostructures recognition.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 2;16(1):244. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55527-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39747880 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering global and local signal generators for probing temporal and spatial cellular signaling dynamics.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 14;11:1239026. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1239026. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37790255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

