Role of hemogram-derived ratios in predicting intensive care unit admission in COVID-19 patients: a multicenter study
- PMID: 35720134
- PMCID: PMC9050181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.04.011
Role of hemogram-derived ratios in predicting intensive care unit admission in COVID-19 patients: a multicenter study
Abstract
Purpose: As hyperinflammation is recognized as a driver of severe COVID-19 disease, checking markers of inflammation is gaining more attention. Our study aimed to evaluate the utility of cost-effective hemogram-derived ratios in predicting intensive care unit (ICU) admission in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: This multicenter retrospective study included hospitalized COVID-19 patients from four dedicated COVID-19 hospitals in Sylhet, Bangladesh. Data on demographics, clinical characteristics, laboratory parameters and survival outcomes were analyzed. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify the significance of each hemogram-derived ratio in predicting ICU admission.
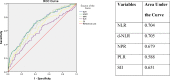
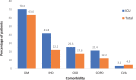
Results: Of 442 included patients, 98 (22.17%) required ICU admission. At the time of admission, patients requiring ICU had a higher neutrophil count and lower lymphocyte and platelet counts than patients not requiring ICU. Peripheral capillary oxygen saturation at admission was significantly lower in those who subsequently required ICU admission. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil-to-platelet ratio, and systemic immune-inflammation index were significant predictors of ICU admission.
Conclusion: Hemogram-derived ratios can be an effective tool in facilitating the early categorization of at-risk patients, enabling timely measures to be taken early in the disease course.
Keywords: COVID-19; ICU admission; hemogram-derived ratios.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemogram-derived ratios as prognostic markers of ICU admission in COVID-19.BMC Emerg Med. 2021 Jul 27;21(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12873-021-00480-w. BMC Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 34315437 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of hemogram-derived ratios for predicting in-hospital mortality in COVID-19: A multicenter study.Health Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 7;5(4):e663. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.663. eCollection 2022 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35686199 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of mortality and ICU requirement in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes: A multicentre study.Nurs Open. 2023 May;10(5):3178-3190. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1567. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Nurs Open. 2023. PMID: 36575597 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the derived isohemagglutinin parameter to predict patients with COVID-19 in need of an intensive care unit.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2022;47(1):73-83. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2022.115091. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35600159 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Blood Indexes of Systemic Inflammation as a Mirror to Admission to Intensive Care Unit in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicentric Study.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2022 Mar;12(1):64-73. doi: 10.1007/s44197-021-00021-5. Epub 2021 Dec 13. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 34904189 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systemic inflammation index, disease severity, and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 21;14:1212998. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1212998. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37415980 Free PMC article.
-
Hemogram-Derived Inflammatory Markers in Cats with Chronic Kidney Disease.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;14(12):1813. doi: 10.3390/ani14121813. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929432 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hemogram-derived Ratios in COVID-19 Severity Stratification in a Primary Healthcare Facility.Acta Inform Med. 2023 Mar;31(1):41-47. doi: 10.5455/aim.2023.31.41-47. Acta Inform Med. 2023. PMID: 37038490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatip A., Kamel M., Hamza M., Farag E., Yassin H., Elayashy M., et al. The diagnostic and prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Review Of Molecular Diagnostics. 2021;21(5):505–514. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2021.1915773. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials