Repositioning Practice of Bedridden Patients: An Evolutionary Concept Analysis
- PMID: 35720208
- PMCID: PMC9201313
- DOI: 10.1177/23779608221106443
Repositioning Practice of Bedridden Patients: An Evolutionary Concept Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Repositioning practice is an essential pressure ulcer prevention intervention that has emerged in the history of nursing. Numerous terms are employed to indicate its meaning, such as turning, positioning, or posturing. However, there is no available analysis that distinguishes these terms or analyzes repositioning practice attributes.
Objective: To analyze repositioning practice as a concept of bedridden patients in hospitals by combining methods from Foucault's archeology of knowledge and Rodger's concept analysis.
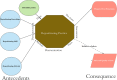
Concept description: Repositioning practice passes through three eras: classical, modern, and research. The repositioning practice is "turn a bedridden patient in a harmonized way and ends with anchor and documentation." The analysis concludes seven attributes for the repositioning practice: pre-turn, assessment, turn, harmonization, anchor, documentation, and time. The analysis assumes bedridden patients, and assigned nurses on duty are the antecedents. Moreover, the main consequence is pressure ulcer prevention, while patient safety and quality of care are the secondary consequences.
Discussion: Repositioning practice understanding has grown with time. Each era has added to or removed from nursing's understanding for repositioning practice until it appears as it now. The current analysis expects further development in repositioning practice understanding and applications.
Conclusion: Repositioning practice is an important nursing intervention and has shown a dynamic movement over history. It is expected that this dynamic will continue in the future.
Keywords: bedridden; patient safety; pressure ulcer; quality of health care.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
-
- Ali K. A. G., Helal W. E. S. H., Salem F. A., Attia H. (2018). Applying interdisciplinary team approach for pressure ulcer assessment, prevention and management. International Journal of Novel Research in Healthcare and Nursing, 5(3), 640–658. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331715726
-
- Baillie L. (2011). Developing practical adult nursing skills third edition. CRC Press.
-
- Baillie L., Ozenbaugh R. L., Pullen T. M. (2014). Developing practical nursing skills. CRC Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources