One Stone, Two Birds: N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Leukemia Stem Cells and the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 35720276
- PMCID: PMC9201081
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.912526
One Stone, Two Birds: N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Leukemia Stem Cells and the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
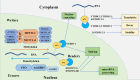
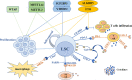
Acute myeloid leukemia is the most common acute leukemia in adults, with accumulation of abundant blasts and impairment of hematogenic function. Despite great advances in diagnosis and therapy, the overall survival of patients with acute myeloid leukemia remains poor. Leukemia stem cells are the root cause of relapse and chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia. The tumor immune microenvironment is another trigger to induce recurrence and drug resistance. Understanding the underlying factors influencing leukemia stem cells and the tumor immune microenvironment is an urgent and unmet need. Intriguingly, N6-methyladenosine, the most widespread internal mRNA modification in eukaryotes, is found to regulate both leukemia stem cells and the tumor immune microenvironment. Methyltransferases and demethylases cooperatively make N6-methyladenosine modification reversible and dynamic. Increasing evidence demonstrates that N6-methyladenosine modification extensively participates in tumorigenesis and progression in various cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia. In this review, we summarize the current progress in studies on the functions of N6-methyladenosine modification in acute myeloid leukemia, especially in leukemia stem cells and the tumor immune microenvironment. We generalize the landscape of N6-methyladenosine modification in self-renewal of leukemia stem cells and immune microenvironment regulation, as well as in the initiation, growth, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of leukemia cells. In addition, we further explore the clinical application of N6-methyladenosine modification in diagnosis, prognostic stratification, and effect evaluation. Considering the roles of N6-methyladenosine modification in leukemia stem cells and the tumor immune microenvironment, we propose targeting N6-methyladenosine regulators as one stone to kill two birds for acute myeloid leukemia treatment.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; RNA methylation; acute myeloid leukemia; leukemia stem cells; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Ouyang and Gong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functions of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modifications in acute myeloid leukemia.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Oct 1;116(4):662-671. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae106. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38721720 Review.
-
m6A Regulator-Mediated Methylation Modification Patterns and Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration Characterization in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 23;12:789914. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.789914. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34887874 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment: Novel Implications for Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 9;12:773570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.773570. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in acute myeloid leukemia.Biomark Res. 2021 May 17;9(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00293-w. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 34001273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated analysis of single-cell RNA-seq and bulk RNA-seq reveals RNA N6-methyladenosine modification associated with prognosis and drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1281687. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1281687. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022588 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of immune-related lncRNAs in AML patients uncovers potential therapeutic targets and prognostic biomarkers.Heliyon. 2024 May 7;10(9):e30616. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30616. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38774083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Döhner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Büchner T, Burnett AK, et al. . Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Adults: Recommendations From an International Expert Panel, on Behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood (2010) 115(3):453–74. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-235358 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

