Bothrops jararaca Snake Venom Inflammation Induced in Human Whole Blood: Role of the Complement System
- PMID: 35720304
- PMCID: PMC9201114
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.885223
Bothrops jararaca Snake Venom Inflammation Induced in Human Whole Blood: Role of the Complement System
Abstract
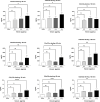
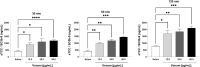
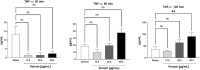
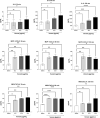
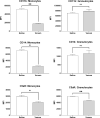
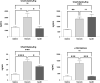
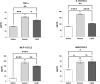
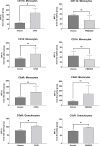
The clinical manifestations of envenomation by Bothrops species are complex and characterized by prominent local effects that can progress to tissue loss, physical disability, or amputation. Systemic signs can also occur, such as hemorrhage, coagulopathy, shock, and acute kidney failure. The rapid development of local clinical manifestations is accompanied by the presence of mediators of the inflammatory process originating from tissues damaged by the bothropic venom. Considering the important role that the complement system plays in the inflammatory response, in this study, we analyzed the action of Bothrops jararaca snake venom on the complement system and cell surface receptors involved in innate immunity using an ex vivo human whole blood model. B. jararaca venom was able to induce activation of the complement system in the human whole blood model and promoted a significant increase in the production of anaphylatoxins C3a/C3a-desArg, C4a/C4a-desArg, C5a/C5a-desArg and sTCC. In leukocytes, the venom of B. jararaca reduced the expression of CD11b, CD14 and C5aR1. Inhibition of the C3 component by Cp40, an inhibitor of C3, resulted in a reduction of C3a/C3a-desArg, C5a/C5a-desArg and sTCC to basal levels in samples stimulated with the venom. Exposure to B. jararaca venom induced the production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines such as TNF-α, IL-8/CXCL8, MCP-1/CCL2 and MIG/CXCL9 in the human whole blood model. Treatment with Cp40 promoted a significant reduction in the production of TNF-α, IL-8/CXCL8 and MCP-1/CCL2. C5aR1 inhibition with PMX205 also promoted a reduction of TNF-α and IL-8/CXCL8 to basal levels in the samples stimulated with venom. In conclusion, the data presented here suggest that the activation of the complement system promoted by the venom of the snake B. jararaca in the human whole blood model significantly contributes to the inflammatory process. The control of several inflammatory parameters using Cp40, an inhibitor of the C3 component, and PMX205, a C5aR1 antagonist, indicates that complement inhibition may represent a potential therapeutic tool in B. jararaca envenoming.
Keywords: Bothrops jararaca; complement system and inhibitors; human whole blood; inflammation; snake venom.
Copyright © 2022 Leonel, Gabrili, Squaiella-Baptistão, Woodruff, Lambris and Tambourgi.
Conflict of interest statement
JL is the founder of Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, which is developing complement inhibitors for therapeutic purposes; is the inventor of patents or patent applications that describe the use of complement inhibitors for therapeutic purposes, some of which are being developed by Amyndas Pharmaceuticals; is the inventor of the compstatin technology licensed to Apellis Pharmaceuticals (Cp05/POT-4/APL-1 and PEGylated derivatives such as APL-2/pegcetacoplan and APL-9). TW is an inventor on patents pertaining to complement inhibitors for inflammatory diseases. He has previously consulted to Alsonex Pty Ltd (who are developing PMX205), but holds not shares, stocks or other commercial interest in this company. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complement System Inhibition Modulates the Pro-Inflammatory Effects of a Snake Venom Metalloproteinase.Front Immunol. 2019 May 22;10:1137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01137. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31231362 Free PMC article.
-
Cp40-mediated complement C3 inhibition dampens inflammasome activation and inflammatory mediators storm induced by Bitis arietans venom.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Feb 6;147:113701. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113701. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39809101
-
Bothrops lanceolatus snake (Fer-de-lance) venom triggers inflammatory mediators' storm in human blood.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Mar;95(3):1129-1138. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02959-0. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33398417
-
C5a-C5aR1 Axis Activation Drives Envenomation Immunopathology by the Snake Naja annulifera.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 15;12:652242. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.652242. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33936074 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical assessment and pathophysiology of Bothrops venom-related acute kidney injury: a scoping review.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020 Jul 10;26:e20190076. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2019-0076. eCollection 2020. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32704246 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory Profile Associated with Secondary Infection from Bothrops atrox Snakebites in the Brazilian Amazon.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 26;15(9):524. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090524. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755950 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing Nanobodies against Venoms from Naja haje Species Captured in North Africa.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;16(9):393. doi: 10.3390/toxins16090393. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330851 Free PMC article.
-
Complement's involvement in allergic Th2 immunity: a cross-barrier perspective.J Clin Invest. 2025 May 1;135(9):e188352. doi: 10.1172/JCI188352. eCollection 2025 May 1. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 40309766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bothrops venom-induced hemostasis disorders in the rat: Between Scylla and Charybdis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Nov 27;17(11):e0011786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011786. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 38011218 Free PMC article.
-
Terminal Complement Activation Is Induced by Factors Released from Endplate Tissue of Disc Degeneration Patients and Stimulates Expression of Catabolic Enzymes in Annulus Fibrosus Cells.Cells. 2023 Mar 13;12(6):887. doi: 10.3390/cells12060887. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kasturiratne A, Wickremasinghe AR, de Silva N, Gunawardena NK, Pathmeswaran A, Premaratna R, et al. The Global Burden of Snakebite: A Literature Analysis and Modelling Based on Regional Estimates of Envenoming and Deaths. PloS Med (2008) 5:e218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050218 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Snakebite Envenoming: A Strategy for Prevention and Control: Executive Summary. World Health Organization (2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

