Prognostic value of Holliday junction-recognizing protein and its correlation with immune infiltrates in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35720487
- PMCID: PMC9185153
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13353
Prognostic value of Holliday junction-recognizing protein and its correlation with immune infiltrates in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
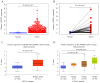
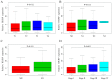
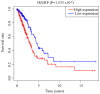
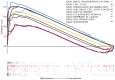
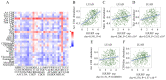
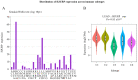
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a disease with high morbidity and mortality rates globally. Holliday junction-recognizing protein (HJURP) has recently been shown to be a potentially useful biomarker for diagnosing and determining the progression and prognosis of different cancer types. The present study assessed the prognostic value of HJURP expression in LUAD and investigated the biological pathways related to HJURP that are involved in LUAD pathogenesis. It was found that high HJURP expression was significantly associated with stage (P=0.001), T grade (P=0.012) and N grade (P=0.012). Overall survival analysis demonstrated that patients with LUAD and high HJURP expression had a worse prognosis compared with those patients with low HJURP expression (P<0.001). Multivariate analysis using the Cox proportional hazards model indicated that the expression of HJURP [hazard ratio (HR), 1.32; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.09-1.60; P=0.004] and stage (HR, 1.90; 95% CI, 1.19-3.03; P=0.007) were independent prognostic factors for patients with LUAD. Gene set enrichment analysis results showed that genes involved with 'basal transcription factors', the 'cell cycle', 'homologous recombination', 'non-small cell lung cancer' (NSCLC), 'oocyte meiosis', 'p53 signaling pathway', 'pathways in cancer', 'RNA degradation' and 'spliceosome' were differentially enriched in the high HJURP expression phenotype. Significant correlations were also found between HJURP and several tumor-infiltrating immune cells, immunomodulators and immune subtypes. Furthermore, western blotting and qPCR analyses confirmed that HJURP was significantly increased in cell lines of NSCLC. In summary, HJURP may be a potentially useful prognostic molecular biomarker of a poor prognosis in LUAD cases. Further experiments are needed to demonstrate the biological effects of HJURP.
Keywords: HJURP; immune infiltration; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
