Efficacy and safety of anlotinib as a third-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 35720500
- PMCID: PMC9185159
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13350
Efficacy and safety of anlotinib as a third-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
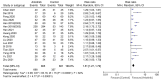
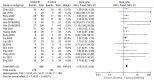
Anlotinib is a novel multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which has been indicated to inhibit both tumor angiogenesis and signal transduction pathways associated with proliferation. The main proposed mechanism of anlotinib inhibiting tumor angiogenesis is that anlotinib inhibits the activation of VEGFR2, PDGFRβ and FGFR1, and downstream ERK signal transduction. The aim of the present study was to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of third-line treatment with anlotinib for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). To meet this aim, studies published up to February 2022 were searched in PubMed, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library and several Chinese databases. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included and a metaanalysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software. A total of 18 RCTs were identified and included in the present study, comprising 1,658 patients. The anlotinib treatment group was indicated to be better than the control group at prolonging progression-free survival [hazard ratio (HR), 0.33; 95% confidence interval (95% CI), 0.28-0.37] and overall survival (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.60-0.81). Anlotinib also provided a significant improvement in the disease control rate [risk ratio (RR), 1.51; 95% CI, 1.27-1.79], objective response rate (1.75, 95% CI, 1.51-2.03) and Karnofsky performance status (mean difference, 9.85; 95% CI, 6.26-13.43). Compared with the control group, the incidence of adverse events (AEs), such as hypertension and hemoptysis, was increased by anlotinib. Through subgroup analysis, it was determined that, compared with the placebo, the incidence of AEs was increased by anlotinib, although compared with other therapeutic drugs, no significant differences were observed. In conclusion, the findings of the present study suggested that the thirdline treatment of advanced NSCLC with anlotinib is more effective compared with other control measures and that the AEs are also controllable. However, given the limitations of the quantity and the quality of the included studies, further studies are required to gain a more complete understanding of the effects of anlotinib.
Keywords: advanced non-small cell lung cancer; anlotinib; meta-analysis; thirdline therapy.
Copyright: © Zha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
