The Ups and Downs of Plant NLR Expression During Pathogen Infection
- PMID: 35720583
- PMCID: PMC9201817
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.921148
The Ups and Downs of Plant NLR Expression During Pathogen Infection
Abstract
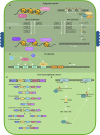
Plant Nucleotide binding-Leucine rich repeat (NLR) proteins play a significant role in pathogen detection and the activation of effector-triggered immunity. NLR regulation has mainly been studied at a protein level, with large knowledge gaps remaining regarding the transcriptional control of NLR genes. The mis-regulation of NLR gene expression may lead to the inability of plants to recognize pathogen infection, lower levels of immune response activation, and ultimately plant susceptibility. This highlights the importance of understanding all aspects of NLR regulation. Three main mechanisms have been shown to control NLR expression: epigenetic modifications, cis elements which bind transcription factors, and post-transcriptional modifications. In this review, we aim to provide an overview of these mechanisms known to control NLR expression, and those which contribute toward successful immune responses. Furthermore, we discuss how pathogens can interfere with NLR expression to increase pathogen virulence. Understanding how these molecular mechanisms control NLR expression would contribute significantly toward building a complete picture of how plant immune responses are activated during pathogen infection-knowledge which can be applied during crop breeding programs aimed to increase resistance toward numerous plant pathogens.
Keywords: NB-LRR; NLR; NLR expression; cis elements; epigenetics; pathogen infection; transcriptional regulatinon.
Copyright © 2022 Fick, Swart and van den Berg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Andam A., Azizi A., Majdi M., Abdolahzadeh J. (2020). Comparative expression profile of some putative resistance genes of chickpea genotypes in response to ascomycete fungus, Ascochyta rabiei (Pass.) Labr. Rev. Bras. Bot. 43, 123–130. doi: 10.1007/s40415-020-00576-w - DOI
-
- Annacondia M. L., Markovic D., Reig Valiente J., Scaltsoyiannes V., Pieterse C., Ninkovic V., et al. . (2021). Aphid feeding induces the relaxation of epigenetic control and the associated regulation of the defence response in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 230, 1185–1200. doi: 10.1111/nph.17226, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

