Physiological, Biochemical, and Yield Responses of Linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) in α-Tocopherol-Mediated Alleviation of Salinity Stress
- PMID: 35720587
- PMCID: PMC9204098
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.867172
Physiological, Biochemical, and Yield Responses of Linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) in α-Tocopherol-Mediated Alleviation of Salinity Stress
Abstract
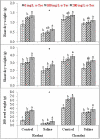
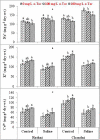
Exogenous application of antioxidants can be helpful for plants to resist salinity, which can be a potentially simple, economical, and culturally feasible approach, compared with introgression and genetic engineering. Foliar spraying of alpha-tocopherol (α-tocopherol) is an approach to improve plant growth under salinity stress. Alpha-tocopherol acts as an antioxidant preventing salinity-induced cellular oxidation. This study was designed to investigate the negative effects of salinity (0 and 120mM NaCl) on linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) and their alleviation by foliar spraying of α-tocopherol (0, 100, and 200mg L-1). Seeds of varieties "Chandni and Roshni" were grown in sand-filled plastic pots, laid in a completely randomized design in a factorial arrangement, and each treatment was replicated three times. Salinity significantly affected linseed morphology and yield by reducing shoot and root dry weights, photosynthetic pigment (Chl. a, Chl. b, total Chl., and carotenoids) contents, mineral ion (Ca2+, K+) uptake, and 100-seed weight. Concomitantly, salinity increased Na+, proline, soluble protein, peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase activities in both varieties. Conversely, the growth and yield of linseed varieties were significantly restored by foliar spraying of α-tocopherol under saline conditions, improving shoot and root dry matter accumulation, photosynthetic pigment, mineral ion, proline, soluble protein contents, peroxidase, catalase, superoxide dismutase activities, and 100-seed weight. Moreover, foliar spray of α-tocopherol alleviated the effects of salinity stress by reducing the Na+ concentration and enhancing K+ and Ca2+ uptake. The Chandni variety performed better than the Roshni, for all growth and physiological parameters studied. Foliar spray of α-tocopherol (200mg L-1) alleviated salinity effects by improving the antioxidant potential of linseed varieties, which ultimately restored growth and yield. Therefore, the use of α-tocopherol may enhance the productivity of linseed and other crops under saline soils.
Keywords: enzymatic antioxidants; foliar application; linseed; saline; α-tocopherol.
Copyright © 2022 Abdullah, Mahmood, Bibi, Naqve, Javaid, Zia, Jabbar, Ud-Din, Attia, Khan, Al-Doss and Fiaz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer SF declared a shared affiliation with the author SF to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed K. B. M., Singh S., Sadiq Y., Khan M. M. A., Uddin M., Naeem M. (2021). Photosynthetic and cellular responses in plants under saline conditions. Front. Plant Soil Interact. 2021, 293–365. 10.1016/B978-0-323-90943-3.00007-9 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

