Altered Default Mode Network Functional Connectivity in Parkinson's Disease: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
- PMID: 35720728
- PMCID: PMC9204219
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.905121
Altered Default Mode Network Functional Connectivity in Parkinson's Disease: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Abstract
Purpose: Whether the intrinsic functional connectivity pattern of the default mode network (DMN) is involved in the progression of cognitive decline in Parkinson's disease (PD) remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the intrinsic functional connectivity (FC) pattern of the DMN anchored on the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) in patients with PD by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI).
Methods: Fifty patients with PD and 50 healthy controls (HCs) were included for resting-state fMRI scanning. A seed-based FC method was used to reveal FC patterns in the DMN with region of interest (ROI) in the PCC. Relationships between FC patterns and disease severity (UPDRS-III) were detected.
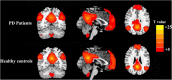
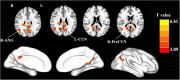
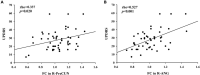
Results: Compared with the HCs, the patients with PD showed increased FC between the PCC and the right precuneus, left cuneus, and right angular gyrus. In the PD group, the increased FC values in the right precuneus were significantly and positively correlated with motor severity as assessed with UPDRS-III scores (rho = 0.337, p = 0.02).
Conclusion: Our result highlights that the patients with PD showed increased FC between the PCC and the right precuneus, left cuneus, and right angular gyrus in the DMN. The altered connectivity pattern in the DMN may play a crucial role in the neurophysiological mechanism of cognitive decline in patients with PD. These findings might provide new insights into neural mechanisms of cognitive decline in PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; cognitive decline; default mode network; functional connectivity; functional magnetic resonance imaging.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Huang, Ma and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer ZX declared a past co-authorship with the author Y-CC to the handling editor.
Figures
References
-
- Bloem B. R., Okun M. S., Klein C. (2021). Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 397 2284–2303. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

