Machine Learning to Analyze Factors Associated With Ten-Year Graft Survival of Keratoplasty for Cornea Endothelial Disease
- PMID: 35721073
- PMCID: PMC9200960
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.831352
Machine Learning to Analyze Factors Associated With Ten-Year Graft Survival of Keratoplasty for Cornea Endothelial Disease
Abstract
Purpose: Machine learning analysis of factors associated with 10-year graft survival of Descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (DSAEK) and penetrating keratoplasty (PK) in Asian eyes.
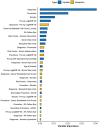
Methods: Prospective study of donor characteristics, clinical outcomes and complications from consecutive patients (n = 1,335) who underwent DSAEK (946 eyes) or PK (389 eyes) for Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy (FED) or bullous keratopathy (BK) were analyzed. Random survival forests (RSF) analysis using the highest variable importance (VIMP) factors were determined to develop the optimal Cox proportional hazards regression model. Main outcome measure was 10-year graft survival with RSF analysis of factors associated with graft failure.
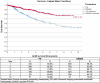
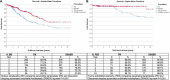
Results: Mean age was 68 ± 11 years, 47.6% male, in our predominantly Chinese (76.6%) Asian cohort, with more BK compared to FED (62.2 vs. 37.8%, P < 0.001). Overall 10-year survival for DSAEK was superior to PK (73.6 vs. 50.9%, log-rank P < 0.001). RSF based on VIMP (best Harrell C statistic: 0.701) with multivariable modeling revealed that BK (HR:2.84, 95%CI:1.89-4.26; P < 0.001), PK (HR: 1.64, 95%CI:1.19-2.27; P = 0.002), male recipients (HR:1.75, 95%CI:1.31-2.34; P < 0.001) and poor pre-operative visual acuity (HR: 1.60, 95%CI:1.15-2.22, P = 0.005) were associated with graft failure. Ten-year cumulative incidence of complications such as immune-mediated graft rejection (P < 0.001), epitheliopathy (P < 0.001), and wound dehiscence (P = 0.002) were greater in the PK compared to the DSAEK group.
Conclusion: In our study, RSF combined with Cox regression was superior to traditional regression techniques alone in analyzing a large number of high-dimensional factors associated with 10-year corneal graft survival in Asian eyes with cornea endothelial disease.
Keywords: endothelial (dys)function; graft survival; keratoplasty; machine learning; penetrating keratoplasty.
Copyright © 2022 Ang, He, Lang, Sabanayagam, Cheng, Arundhati and Mehta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

