Ethnomedicinal, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Investigations of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd (Lamiaceae)
- PMID: 35721148
- PMCID: PMC9201335
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.896078
Ethnomedicinal, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Investigations of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd (Lamiaceae)
Abstract
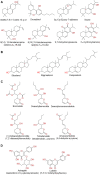
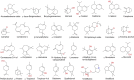
Tetradenia riparia Hochsteter codd. (Lamiaceae) in its native African continent, is considered one of the most popular aromatic medicinal plants. In folk medicine it may be used as an infusion to treat respiratory problems, cough, headache, stomach pain, diarrhea, fever, malaria, and dengue; and in the form of compresses it is applied for the relief of headaches and toothaches. The species T. riparia has been researched for decades to isolate and identify chemical constituents present in extracts or essential oil obtained from the leaves, floral buds, or stems of this plant. The present study reviews the scientific literature on ethnomedicinal, phytochemical, and pharmacological aspects of T. riparia. We discuss issues related to the botanical and geographical description of the species, ethnobotanical uses, phytochemical studies on its essential oil and extracts, and biological activities of T. riparia. Several compounds have already been isolated from leaves, such as ibozol, 7α-hydroxyroileanone, 1',2'-dideacetylboronolide, 8(14),15-sandaracopimaradiene-7α,18-diol; 5,6-dihydro-α-pyrone and α-pyrone. Terpenes predominated in the essential oil, comprising monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, hydrocarbons, and oxygenates. Most phytocompounds were isolated from the leaves and flower buds, namely fenchone, 14-hydroxy-9-epi (E)-caryophyllene, 9β, 13β-epoxy-7-abietene, and 6,7-dehydroroileanone. These compounds provide the species a high pharmacological potential, with antimicrobial, antioxidant, antitumor, analgesic, anti-leishmania, anti-tuberculosis, and anti-parasitic activities. Therefore, this species is a promising herbal medicine.
Keywords: 14-hydroxy-9-epi(E)-caryophyllene; 6,7-dehydroroileanone; 8(14),15sandaracopimaradiene-7 α, 18-diol; computational analysis; diterpenes; ethnopharmacology; traditional folk medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Panda, Gazim, Swain, Bento, Sena, Mukazayire, Van Puyvelde and Luyten.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



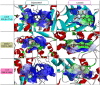
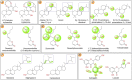
References
-
- Araújo L. L. N., Melo H. C., Paula J. R., Alves F. R. R., Portes T. A. (2018). Yield and Composition of the Essential Oil of Tetradenia Riparia (Hochst) Codd (Lamiaceae) Cultivated under Different Shading Levels. Planta daninha. 36, e0181647451–9. 10.1590/S0100-83582018360100066 - DOI
-
- Baldin V. P., Scodro R. B. L., Lopes-Ortiz M. A., de Almeida A. L., Gazim Z. C., Ferarrese L., et al. (2018). Anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis Activity of Essential Oil and 6,7-dehydroroyleanone Isolated from Leaves of Tetradenia Riparia (Hochst.) Codd (Lamiaceae). Phytomedicine 147, 34–39. 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.043 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bekalo T. H., Woodmatas S. D., Woldemariam Z. A. (2009). An Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used by Local People in the Lowlands of Konta Special Woreda, Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples Regional State, Ethiopia. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed 5 (26), 26–15. 10.1186/1746-4269-5-26 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blythe E. K., Tabanca N., Demirci B., Kendra P. E. (2020). Chemical Composition of Essential Oil from Tetradenia Riparia and its Attractant Activity for Mediterranean Fruit Fly, Ceratitis Capitata . Nat. Product. Commun. 15 (9), 1934578X2095395–6. 10.1177/1934578X20953955 - DOI
-
- Bodenstein J. W. (1977). Toxicity of Traditional Herbal Remedies. S. Afr. Med. J. 5220, 790. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

