Diagnostic Pearls of Vulvar Epidermolytic Acanthoma: Case Report
- PMID: 35721331
- PMCID: PMC9171174
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2022.34.3.221
Diagnostic Pearls of Vulvar Epidermolytic Acanthoma: Case Report
Abstract
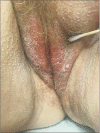
Epidermolytic acanthomas (EA) are uncommon benign tumors clinically presenting as single to multiple papules. Histologically, EA display hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, acanthosis, and epidermal degeneration-also known as epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (EH). EA may be misdiagnosed as condyloma both clinically and histopathologically when located on the genitalia. Thus, this diagnosis carries a significant psychological burden and must remain in the differential when initially considering genital warts. We utilize the case of a 62-year old female referred to dermatology for a 5-year history of multiple pruritic and hypopigmented vulvar papules-misdiagnosed as genital warts-to highlight the impact of differentiating EA from genital warts. This patient was initially misdiagnosed with common genital warts at her gynecologist's office and treated unsuccessfully for years. A shave biopsy was performed and histology revealed EH, consistent with EA.
Keywords: Condylomata acuminata; Epidermolytic acanthoma; Vulvar epidermolytic acanthoma.
Copyright © The Korean Dermatological Association and The Korean Society for Investigative Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Shapiro L, Baraf CS. Isolated epidermolytic acanthoma. A solitary tumor showing granular degeneration. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:220–223. - PubMed
-
- Niizuma K. Isolated epidermolytic acanthoma. A histological study. Dermatologica. 1979;159:30–36. - PubMed
-
- Roy SF, Ghazawi FM, Choate KA, McNiff JM. Solitary and multiple epidermolytic acanthoma: a demographic and clinical study of 131 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:305–309. - PubMed
-
- Lee TJ, Wu YH. Multiple epidermolytic acanthomas mimicking condyloma: a retrospective study of 8 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:28–33. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

